Researchers from the group of Prof. Carles Bo on the Institute of Chemical Analysis of Catalonia (ICIQ-CERCA) have described a computational methodology that simulates advanced processes involving totally different chemical species and numerous situations. These processes result in the formation of nanostructures referred to as polyoxometalates (POMs), with necessary functions in catalysis, power storage, biology and drugs.
The work seems in Chemical Science.
“Our group has lately developed distinctive strategies to check the chemistry of polyoxometalates in answer, their speciation and formation mechanisms. This analysis has the potential to find the experimental situations wanted to make new supplies,” explains Prof. Bo.
Versatile POMs
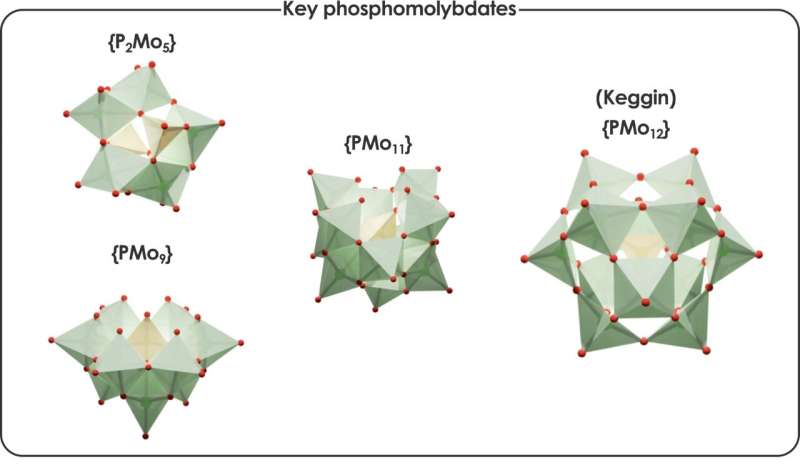
POMs are a distinguished household of nanostructures composed of transition steel atoms linked by oxygens, forming a variety of well-defined buildings of various configurations and dimensions. These nanostructures are fashioned by way of self-assembly processes of easy steel oxides, relying on various factors equivalent to pH, temperature, strain, complete steel focus, ionic pressure, and the presence of lowering brokers and counter-ions. The sum of all these situations complicates the management of their synthesis.
Researchers can now predict the impact of those components and the appropriate situations to supply one particular species of POM, using statistical strategies that facilitate the environment friendly and scalable processing of quite a few speciation fashions and their corresponding methods of non-linear equations. That is necessary, as the primary key software of those nanostructures is expounded to catalysis, the place POMs are recognized to speed up a number of necessary reactions. For instance, utilizing these simulations, it’s attainable to explain the appropriate situations that result in the manufacturing of a species of POM liable for catalyzing CO2 fixation.
POMSimulator
The group of Prof. Bo has introduced an open–supply software program bundle named POMSimulator that helps make clear the formation mechanisms of POMs. By releasing a public model of the code, the researchers purpose to supply a software for complementing the invention of novel POMs. Furthermore, having an accessible model of the code implies that different researchers can modify the supply code primarily based on their wants.

The methodology now introduced is a extra strong model of this POMSimulator that gives new and invaluable insights into the distribution of species beneath totally different chemical situations, thereby enriching the information of advanced methods speciation.
“Within the instances of Massive Information, machine studying and synthetic intelligence, it’s essential to make use of each bit of data in our fingers. Our work has taken POMSimulator to the subsequent stage of information utilization,” mentioned Jordi Buils, first writer of this work and Ph.D. pupil in Prof. Bo’s group.
Extra info:
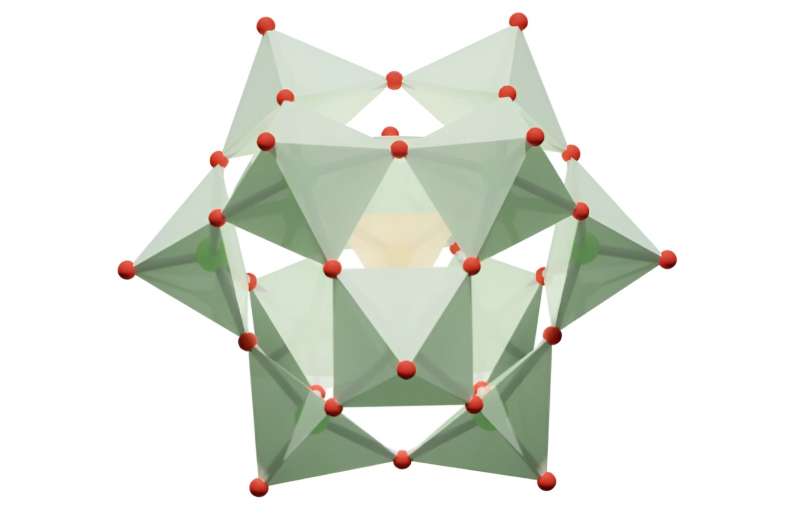
Jordi Buils Casasnovas et al, Computational Insights into Aqueous Speciation of Metallic-Oxide NanoClusters: An In-Depth Examine of the Keggin Phosphomolybdate, Chemical Science (2024). DOI: 10.1039/D4SC03282A
Supplied by
Institute of Chemical Analysis of Catalonia
Quotation:
New computational methodology to foretell the advanced formation of fascinating nanostructures (2024, August 20)
retrieved 20 August 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-08-methodology-complex-formation-nanostructures.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.


