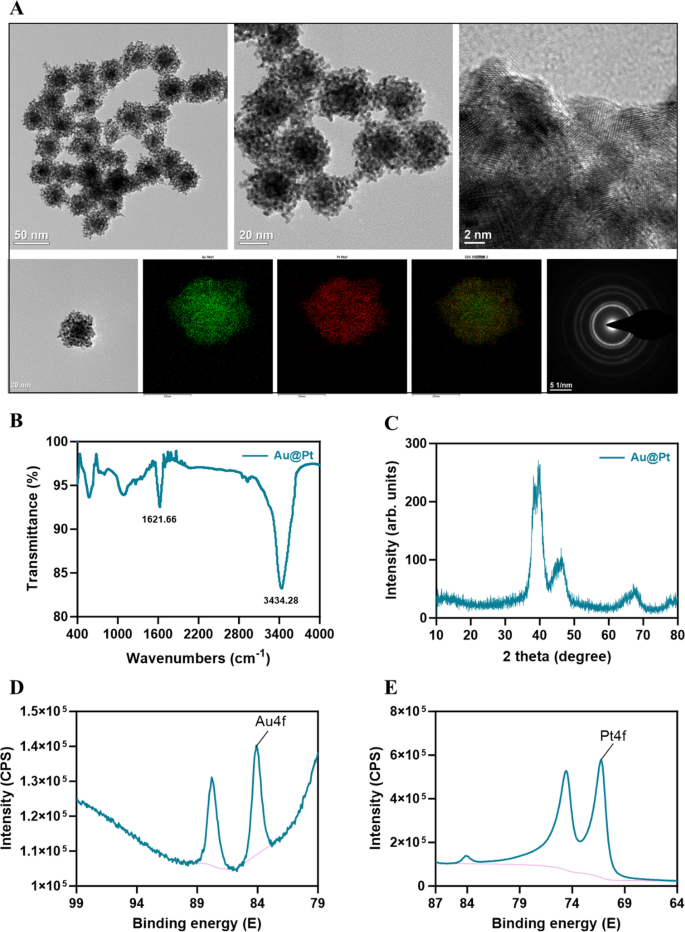
Characterization of Au@Pt nanozyme
Au@Pt nanozyme was synthesized by a one-step co-reduction strategy [33]. As proven within the TEM picture (Fig. 1A), Au@Pt NPs exhibit a dendritic morphology and the diameter was 30–50 nm. We used EDS elemental mapping evaluation to detect the spatial association of the 2 steel parts within the Au@Pt. The inexperienced particles representing Au are extra densely distributed within the heart than within the periphery, thus confirming that Au is predominantly distributed within the nuclear construction. The purple particles representing the ingredient Pt are distributed within the shell (Fig. 1A). Au@Pt is a bimetallic nanoparticle with a core–shell construction that’s extremely mesoporous in nature. FTIR was used to find out potential interactions between floor biomolecules and steel ions, which contribute to the comprehension of the Au@Pt nanozymes’ mechanism of biosynthesis (Fig. 1B). The crystal buildings of the ready samples have been detected by XRD. Determine 1C exhibits the XRD patterns of Au@Pt nanozyme. To grasp the mode of binding additional, we used XPS to analyze the composition of floor parts, structural particulars, and chemical states, as proven in Fig. 1D, E, the principle peaks at 84.08 (4f) and 87.80 (4f) have been attributed to Au0+, whereas the peaks at 74.6 (4f) and 71.25 (4f) have been attribute of Pt0+ species. Most significantly, we discovered that Au@Pt exhibited wonderful POD, CAT, and SOD-like actions.
Au@Pt improves glucose tolerance and reduces TG
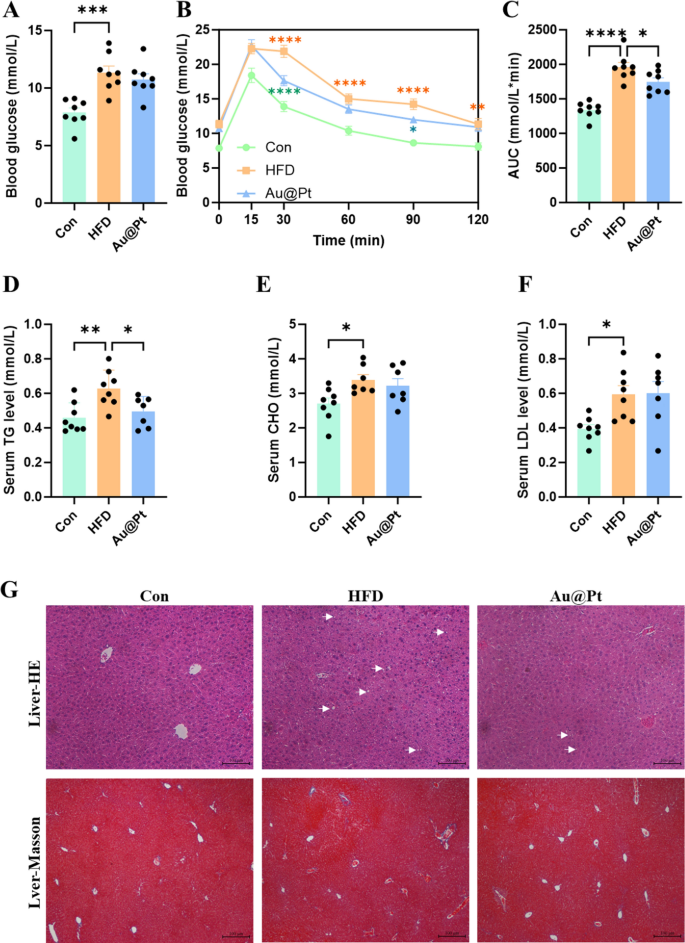
To substantiate the impact of Au@Pt on physique composition, the organ mass was decided in regular food regimen, HFD, and Au@Pt administration group mice. A HFD for 4 weeks resulted in vital will increase in epididymal fats weight, physique weight, inguinal fats weight, visceral fats weight, perirenal fats weight, and adipocyte space in mice (Fig. S2A–2F). Whereas, in comparison with the HFD group, the administration of Au@Pt confirmed a development of decreasing these indicators, however didn’t exhibit vital variations (Fig. S2A–S2F). Given the restricted intervention interval of 4 weeks for Au@Pt, any noticed results on physique weight and organ weight might exhibit a reducing development; nonetheless, no statistically vital variations have been recognized. Future research might use interventions that mimic pure merchandise, resembling weight problems or diabetes fashions earlier than implementing substance interventions [34, 35]. Moreover, extending the length of dietary and materials co-interventions to eight–12 weeks might strengthen the robustness of the findings.
To additional examine the affect of Au@Pt on glucose metabolism, we carried out fasting blood glucose testing in addition to a glucose tolerance check. As proven in Fig. 2A–C, HFD considerably impairs glucose tolerance and will increase the world below the curve (AUC) of OGTT in comparison with a traditional food regimen. Notably, Au@Pt considerably improved glucose tolerance and decreased the AUC of OGTT, however didn’t have an effect on fasting plasma glucose (Fig. 2A–C). In present analysis, metabolic abnormalities induced by a HFD are also proven as the rise of blood lipids (Fig. 2D–F), liver lipid accumulation (Fig. 2G), hypertrophic adipose tissue cells (Fig. S2F and S2J), and unaffected liver weight and liver perform indicators (Fig. S2G-S2I). In the meantime, Au@Pt therapy considerably lowered blood TG ranges, hepatic lipid accumulation, and fibrosis in comparison with the HFD group (Fig. 2D, G). Taken collectively, the analyses above clearly elucidated that Au@Pt improves glucose tolerance and reduces TG.
Transcriptional profiles evaluation of Au@Pt handled mice liver
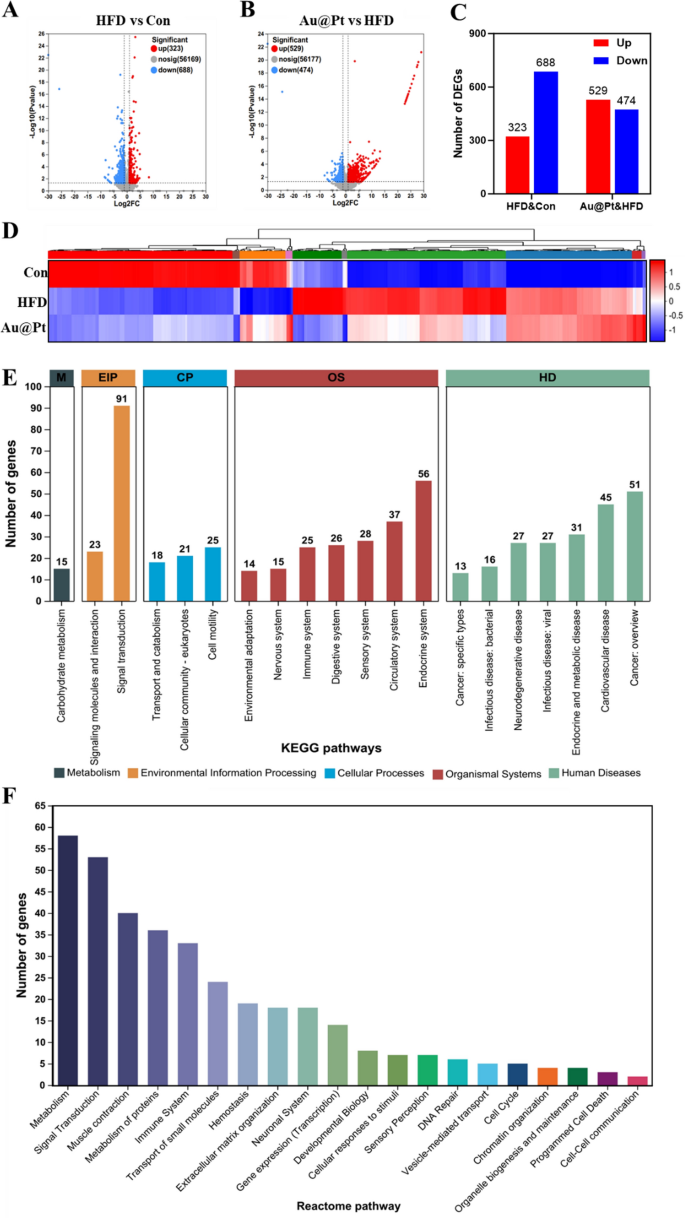
Contemplating that the liver performs a vital function within the physique’s glucose and lipid metabolism [36, 37], to additional discover the development impact of Au@Pt on glucose and lipid metabolism issues, we carried out a transcriptome profile of liver. As illustrated in Fig. 3A–C, between the HFD group and the management group there have been 1011 DEGs, of which 323 had elevated expression and 688 had decreased expression (log2|fold change|> 1 and p < 0.05). In the meantime, Au@Pt administration considerably up-regulated 529 genes and down-regulated 474 genes in comparison with the HFD group (log2|fold change|> 1 and p < 0.05). DEGs heatmaps have been generated to elucidate the consequences of Au@Pt ingestion on gene expression alterations within the liver. As depicted in Fig. 3D, oral administration of Au@Pt successfully reversed the gene expression modifications induced by HFD. Subsequent, we carried out KEGG and Reactome annotation of the DEGs to determine the genes of curiosity for additional evaluation. As proven in Fig. 3E, probably the most considerable phrases associated to environmental info processing (EIP) and organismal techniques (OS) have been related to signaling transduction and the immune system. Notably, the 2 most extremely regulated Reactome pathways have been these associated to metabolism and immune system sign transduction. These outcomes instructed that the principle affect of Au@Pt on the transcriptional profile was targeted on metabolism and sign transduction.
Transcriptomic evaluation of liver. A and B The volcanic map of DEG distribution; C The variety of DEGs; D Warmth map plots for DEGs; E The histogram of KEGG; F Reactome annotations evaluation. HD: Human Illnesses; OS: Organismal Techniques; CP: Mobile Processes; EIP: Environmental Data Processing; M: Metabolism
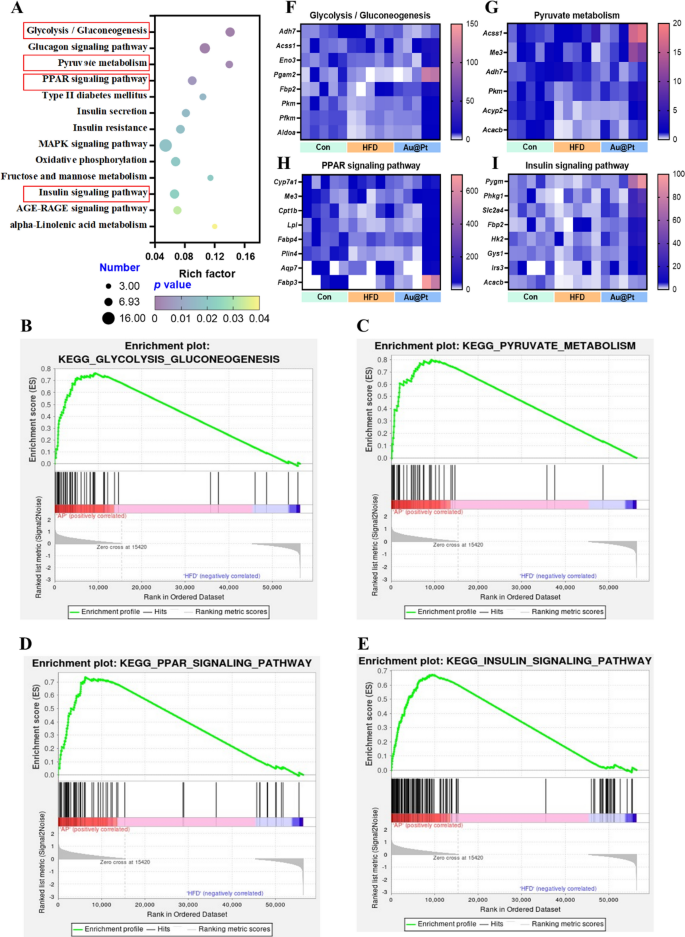
To additional elucidate the main modulation signaling pathways concerned in DEGs, KEGG and GSEA analyses have been carried out, respectively. Firstly, the 13 most necessary KEGG pathway associated to metabolism have been categorised and ranked in keeping with enrichment scores (p < 0.05) (Fig. 4A). There have been 21 totally different signaling pathways between HFD and management group (p < 0.05) and 22 totally different signaling pathways between Au@Pt and HFD group (p < 0.05) (Desk S2). Apparently, within the GSEA evaluation, we enriched 7 necessary signaling pathways, which have been positively correlated with the management group and Au@Pt group and negatively correlated with the HFD group, primarily together with GnRH signaling pathway, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, lysosome, olfactory transduction, glutathione metabolism, long run despair, and neurotrophin signaling pathway (Fig. S3). These outcomes recommend that Au@Pt can change within the course of the Management group by reversing the above signaling pathways affected by HFD.
Notably, our complete evaluation of the above differential gene KEGG-enriched signaling pathways and the gene-wide GSEA signaling pathway recognized 4 intersecting necessary signaling pathways together with glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, pyruvate metabolism, PPAR signaling pathway, and insulin signaling pathway (Fig. 4A–E). Then, the important thing genes enriched in these pathways have been heat-mapped between management, HFD, and Au@Pt group (Fig. 4F–I). Taken collectively, the analyses above clearly elucidated that Au@Pt modulates glucose and lipid metabolism homeostasis could also be related to glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, insulin signaling pathway, PPAR signaling pathway, and pyruvate metabolism. To additional confirm the variations within the above signaling pathways, the expression of key genes was verified by qRT-PCR (Fig. S4).
Evaluation of key genes regulated by Au@Pt within the liver
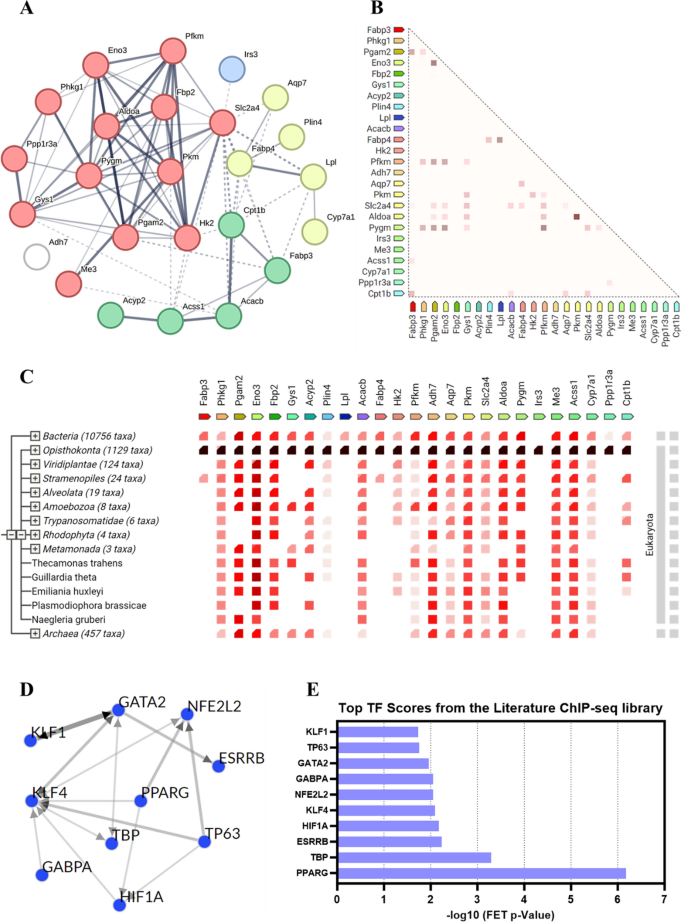
To additional discover how the important thing genes regulated by Au@Pt play a job in modulating the homeostasis of glucose and lipid metabolism within the physique, we chosen 25 genes within the above 4 key signaling pathways for the protein–protein interactions (PPI) evaluation and transcription issue (TF) evaluation. PPI community evaluation was carried out utilizing the STRING 12.0 database to determine the important thing gene targets in key pathways affected by Au@Pt (Desk S3), and the outcomes confirmed that the very best interplay was Pgam2 and Eno3, adopted by Pkm and Aldoa (Fig. 5A). As proven, the proteins with the very best correlation of gene expression are Pkm and Aldoa, adopted by Pgam2 and Eno3 (Fig. 5B). As indicated by cooccurrence interactions, gene households with related patterns seem within the genome (Fig. 5C). TF enrichment was carried out on DEGs in key pathways utilizing ChEA3 to analyze doubtlessly upstream TFs associated to variants noticed within the literature based mostly on CHIP-seq. As proven in Fig. 5D, E, the highest 10 TF from the literature ChIP-seq library as PPARG, TBP, ESRRB, HIF1A, KLF4, NFE2L2, GABPA, GATA2, TP63, and KLF1. Not too long ago, some researchers reported that the regulation of PKM2 and HK2 expression by the PPARg and HIF1α-PPARg axis performs necessary roles in glucose and lipid metabolism, together with mediating glycolysis, liver steatosis, hypertrophy, and hyperplasia [38, 39]. Collectively, the potential function of Au@Pt in glucose and lipid metabolism might have an effect on downstream signaling pathways by regulating TFs resembling HIF1a and PPARg.
The regulatory impact of Au@Pt on glucose and lipid metabolism in hepatocytes
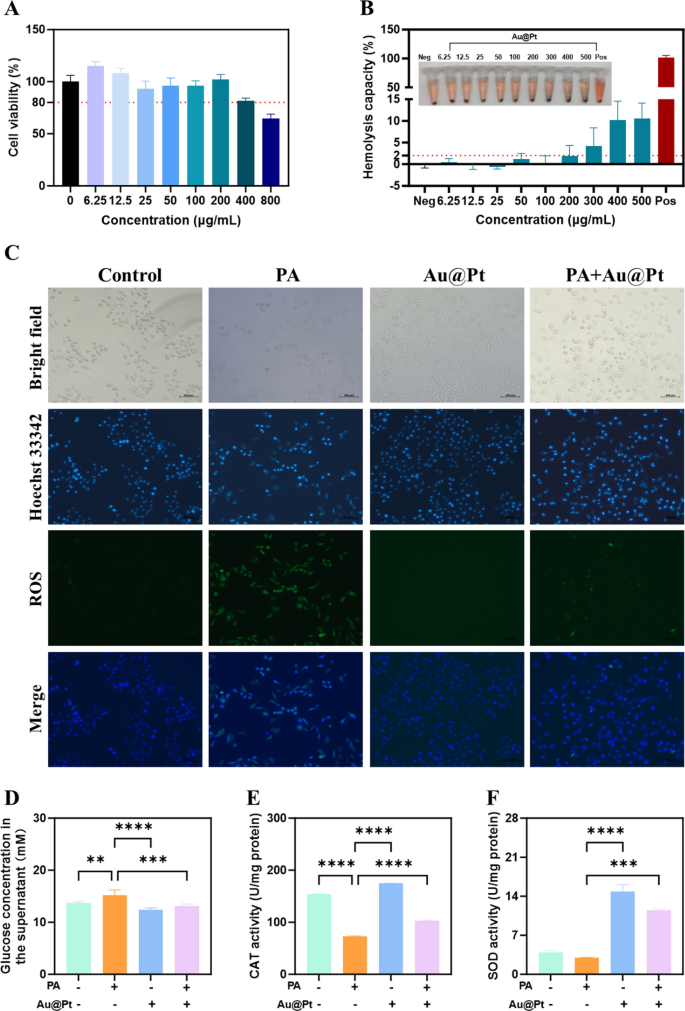
To additional examine the regulatory results of Au@Pt on glucose and lipid metabolism on the mobile degree in vitro, we carried out this experiment in human hepatocyte cell traces HepG2 cell. Firstly, after 24 h of incubation with Au@Pt, HepG2 cells retained > 80% viability throughout Au@Pt at concentrations starting from 0–200 μg/mL (Fig. 6A). Biocompatibility is crucial for the interpretation of nanozymes into scientific purposes [40,41,42]. Then, we incubated rabbit purple blood cells with various Au@Pt concentrations (0–500 μg/mL) at 37 °C for two h to guage the biocompatibility of the Au@Pt within the blood circulation. As proven in Fig. 6B, no vital hemolysis (lower than 2%) was noticed at concentrations from 0 to 200 μg/mL after incubation of Au@Pt with purple blood cell suspension, indicating that the Au@Pt had good organic security. It’s attention-grabbing to notice that in distinction to the overactive ROS era induced by palmitic acid (PA) in HepG2 cells (Fig. 6C), the PA + Au@Pt group confirmed a major discount within the accumulation of ROS. In addition to, in contrast with PA, Au@Pt considerably lowered glucose focus within the supernatant (Fig. 6D). According to the Au@Pt enzyme-like exercise, we discovered that Au@Pt additionally elevated the CAT and SOD exercise below circumstances of PA stimulation (Fig. 6E, F).
The modulation of intestine microbiota by Au@Pt
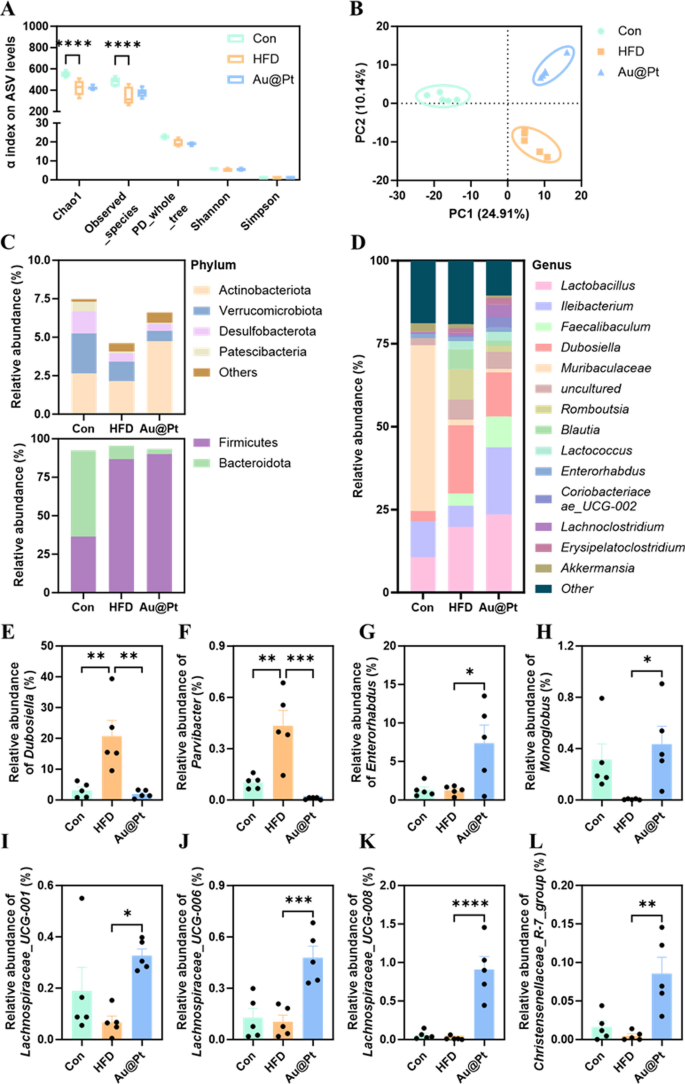
An rising variety of research have proven that issues of the intestine microbiota and its metabolites can severely affect the onset and development of metabolic issues [43,44,45]. To unravel the modulatory results of Au@Pt on the intestine microbiota, high-throughput 16S rRNA gene sequencing of the V3-V4 area was carried out to analyze the modifications within the microbial neighborhood. α-Range evaluation confirmed that the microbial neighborhood of mice within the HFD group confirmed a major lower in variety (Chao and noticed species) and richness (noticed ASVs) in comparison with the management and Au@Pt teams (Fig. 7A). Furthermore, β variety evaluation based mostly on Bray–Curtis revealed that the buildings of the bacterial communities within the Au@Pt-treated mice have been similar to the mice within the management group alongside PC2, the connection between Au@Pt and HFD alongside PC1 seems to be related, and that the teams are certainly dispersed alongside PC2 (Fig. 7B). Adjustments within the construction of the intestine microbiota neighborhood in management, HFD, and Au@Pt mice have been related to altered patterns of relative abundance, which have been seen at each the phylum and genus degree (Fig. 7C, D).
Structural and compositional evaluation of the intestine microbiota. A α variety displayed by noticed ASV ranges; B PLS-DA plot evaluation of β-diversity of the intestine microbiota; The intestine microbiota relative abundance on the C phylum and D genus degree; E–L The relative abundance of Dubosiella, Parvibacter, Enterorhabdus, Monoglobus, Lachnospiraceae_UCG-008, Lachnospiraceae_UCG-006, Lachnospiraceae_UCG-001, and Christensenellaceae_R-7_group at genus ranges
Particularly, we discovered a major improve within the relative abundance of Dubosiella and Parvibacterat genus ranges in HFD-fed mice, whereas Au@Pt administration considerably decreased these relative abundances to be in line with the management group (Fig. 7E, F). Equally, oral consumption Au@Pt considerably elevated the relative abundance of Enterorhabdus, Monoglobus, Lachnospiraceae_UCG-008, Lachnospiraceae_UCG-006, Lachnospiraceae_UCG-001, and Christensenellaceae_R-7_group in contrast with HFD at genus ranges (Fig. 7G–L).
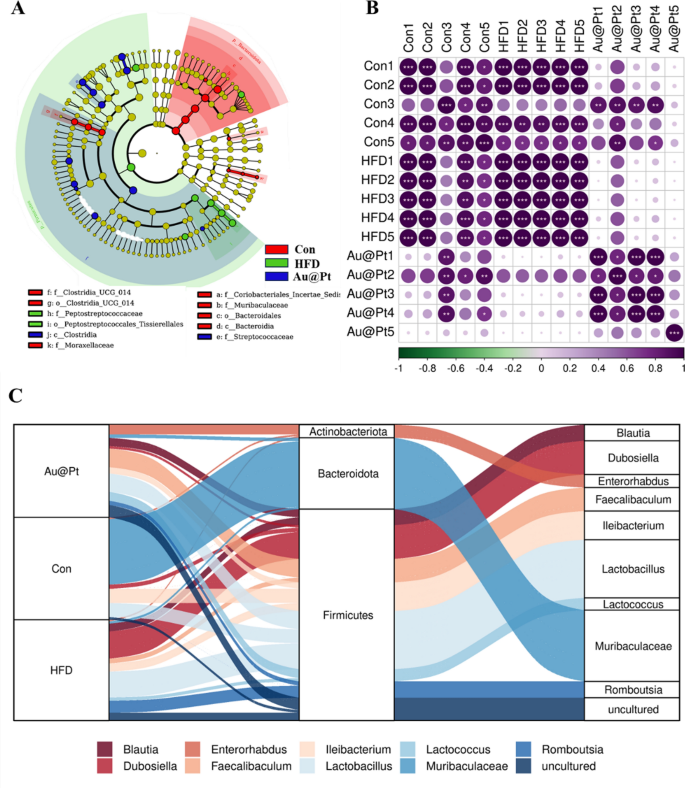
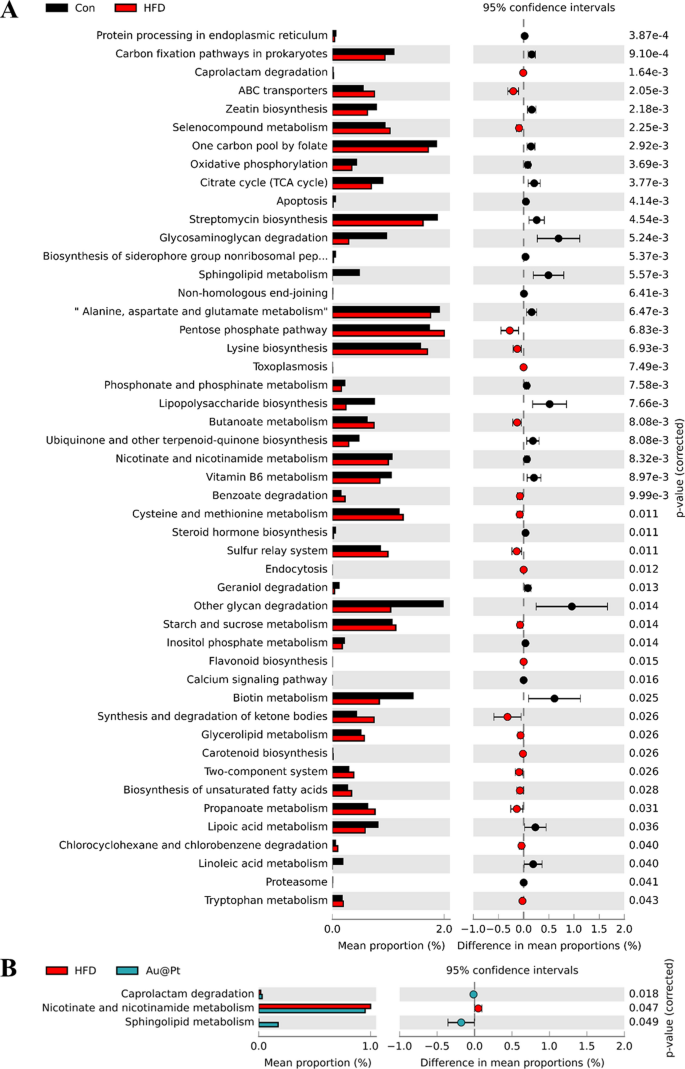
Warmth map of dominant genera was analysed and the outcomes confirmed that the variety of dominant genera confirmed an rising development after Au@Pt therapy (Fig. 8A). To find out the particular taxa of microorganisms affected by Au@Pt in HFD-fed mice, LEfSe analyses have been carried out starting from the phylum degree to the species degree, with significance outlined as p < 0.05 and LDA scores > 4 (Fig. 8B). As well as, the correlation of intestine microbiota among the many three teams additionally indicated that Au@Pt supplementation reversed the modifications induced by a HFD and tended to align extra intently with the management teams and confirmed a optimistic correlation (Fig. 8C). We carried out a radical characterization of the alterations in intestine microbiota composition in HFD-fed mice subjected to therapy with Au@Pt, using Sankey diagrams to visualise the modifications at each the phylum and species ranges (Fig. 8D). In PICRUSt2, 16S rRNA gene sequencing knowledge from the intestine microbiota are coupled with generally obtainable database units to foretell of the practical profile of the intestine microbiota and to create a practical “map” [46, 47]. As proven in Fig. 9A, samples from the HFD group and the management group primarily differed within the following metabolic pathways associated to glucose and lipid metabolism: citrate cycle, phosphonate and phosphinate metabolism, steroid hormone biosynthesis, sucrose, and starch metabolism, biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, propanoate metabolism, lipoic acid metabolism, and linoleic acid metabolism. In comparison with HFD mice, caprolactam degradation, nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism, and sphingolipid metabolism have been considerably altered after Au@Pt administration (Fig. 9B).
The totally different intestine microbiota evaluation at genus ranges. A Bacterial taxa displaying totally different abundances between management, HFD, and Au@Pt group; B The correlation of intestine microbiota amongst management, HFD, and Au@Pt group; C Sankey diagrams analysing the relative abundance of intestine microflora at phylum degree (left) and genus degree (proper) for samples from management, HFD, and Au@Pt teams
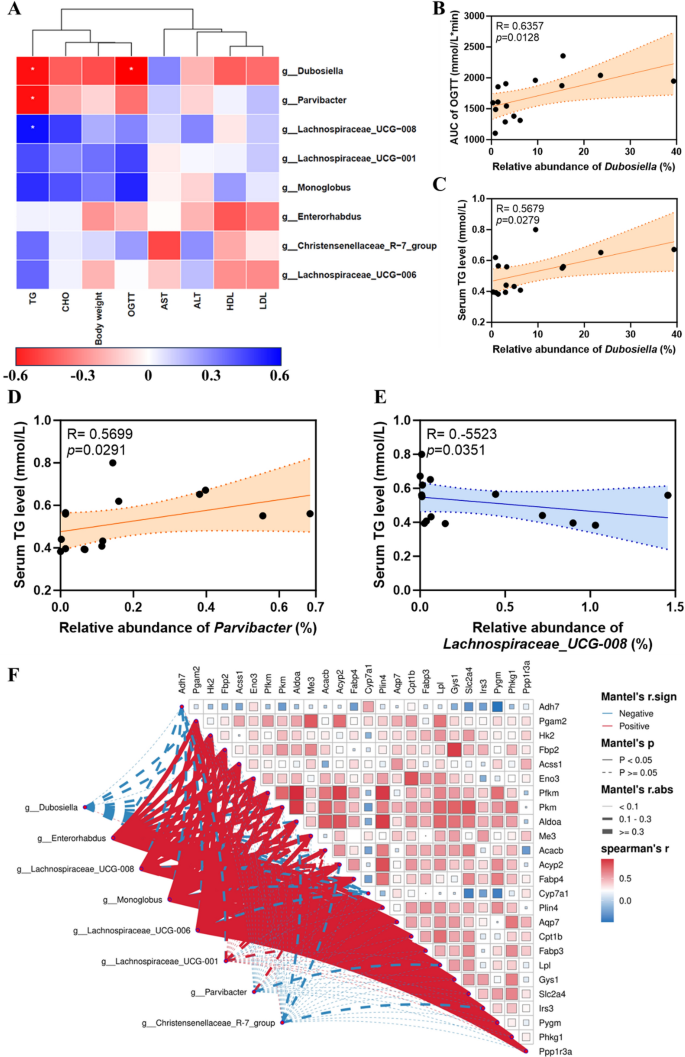
Then, we analysed the affiliation between 16S rRNA outcomes and metabolic indices. The outcomes confirmed that variations in serum TG ranges have been positively correlated with Dubospora and Parvibacter on the taxonomic degree of the genus (Fig. 10A, C, D) however negatively correlated to Lachnospiraceae_UCG-008 (Fig. 10A, E). The distinction within the AUC of OGTT was positively correlated to Dubosiella (Fig. 10A, B). The AUC of OGTT variations had a optimistic correlation with Dubosiella. Taken collectively, these findings recommend that the regulation of Au@Pt on glucose and lipid metabolism could also be related to altered composition and construction of the intestine microbiota. Furthermore, the warmth map of the correlation community additionally instructed that there was an in depth correlation between the differential genes and the differential intestine micro organism (Fig. 10F). General, intestine microbiota could also be an necessary goal for understanding the metabolic homeostasis regulated by Au@Pt, which additionally supplies an necessary theoretical foundation for selling Au@Pt to scientific utility. The usage of nanozyme in modulating the intestine microbiota holds promise for the event of latest methods for selling intestine well being and treating gut-related issues. Further investigations are required to totally perceive nanozymes’ potential on this space and to develop secure and efficient nanozyme-based therapies for modulating intestine microbiota.
Evaluation of correlation between metabolic index and intestine microbiota. A Evaluation of metabolic index with differential intestine microbiota at genus degree; B Spearman’s correlation evaluation of the AUC of OGTT with the relative abundance of Dubosiella; C Spearman’s correlation evaluation of the relative abundance of Dubosiella with serum TG ranges; D Spearman’s correlation evaluation of the relative abundance of Parvibacter with serum TG ranges; E Spearman’s correlation evaluation of the relative abundance of Lachnospiraceae_UCG-008 with serum TG ranges; F The warmth map of correlation community of differential genes and differential intestine micro organism
The pharmacokinetic and biosafety evaluation of Au@Pt
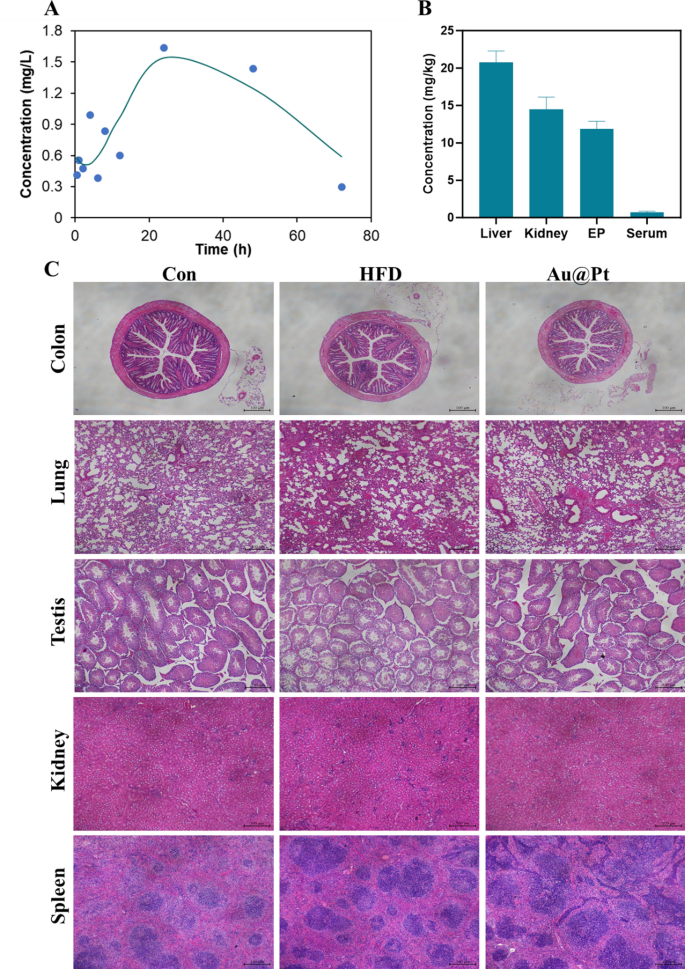
The pharmacokinetics and the in vivo metabolic profile of Au@Pt in a mouse mannequin have been investigated. To evaluate the circulatory scenario of Au@Pt, we carried out measurements of the Pt ingredient content material within the serum at totally different time factors (0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h) utilizing ICP-MS. As proven in Fig. 11A and Desk S4, the elimination half-life (t1/2) of Au@Pt was calculated as 13.506 h in a two-compartment pharmacokinetic mannequin. The imply residence time (MRT) and the time to peak (Tmax) of Au@Pt within the physique have been decided to be 57.437 h and 24 h based mostly on the pharmacokinetics knowledge respectively. Subsequently, we measured the degrees of Au@Pt in several tissues after administered for 4 weeks, and the information from the research indicated that the very best ranges have been within the liver, adopted by the kidney and epididymal fats, and decrease ranges within the serum relative to the totally different tissues (Fig. 11B).
The biosafety of Au@Pt is important for future purposes, particularly for scientific therapy. Firstly, we evaluated the biocompatibility of Au@Pt in vitro, as proven in Fig. 6D, no vital hemolysis (lower than 2%) was noticed after incubation of Au@Pt with purple blood cell suspension, indicating that the Au@Pt had good organic security. As well as, we have now carried out a number of research on the biosafety of Au@Pt throughout in vivo experiments. Based on the totally different organ weights (Fig. S2), the Au@Pt didn’t affect the load modifications of organ tissue. Analyses of blood biochemistry revealed that Au@Pt didn’t impair liver biochemistry and performance, kidney perform, or different serum parameters (Fig. 11A–F). Equally, there was no seen pathological harm to the organ tissues as revealed by H&E staining (Fig. 11C). These observations recommend that the minimal and even undetectable toxicity of Au@Pt in vitro and in vivo suggests its potential utility within the upkeep of metabolic homeostasis. Nanozyme’s distinctive properties on the nanoscale can also pose dangers, notably concerning neurotoxicity. For instance, mobile interactions, oxidative stress, inflammatory response, passage throughout the blood–mind barrier, and long-term results. Contemplating these elements, a radical investigation into the neurotoxic results of nanozymes is crucial to make sure their security in medical purposes. Future research ought to concentrate on elucidating the mechanisms of neurotoxicity, assessing the consequences on neuronal well being, and establishing security benchmarks for his or her use in vivo.