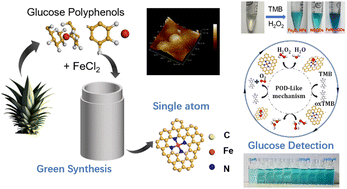
Single-atom nanozymes with well-defined atomic constructions and digital coordination environments can successfully mimic the capabilities of pure enzymes. Nevertheless, the pricey and complex preparation processes have hindered additional exploration and software of those single-atom nanozymes. On this research, we offered a synthesis approach for creating Fe–N central single-atom doped graphene quantum dot (FeN/GQDs) nanozymes utilizing a one-step solvothermal course of, the place particular person iron atoms kind sturdy bonds with graphene quantum dots by way of nitrogen coordination. Not like earlier research, this technique considerably simplifies the synthesis circumstances for single-atom nanozymes, eliminating the necessity for prime temperatures and using environmentally pleasant precursors derived from pineapple (ananas comosus) leaves. The ensuing FeN/GQDs exhibited peroxidase-like catalytic exercise and kinetics corresponding to that of pure enzymes, effectively changing H2O2 into hydroxyl radical species. Leveraging their wonderful peroxide-like exercise, FeN/GQDs nanozymes have been efficiently utilized to assemble a colorimetric biosensor system characterised by remarkably excessive sensitivity for glucose detection. This achievement demonstrated a promising method to designing single-atom nanozymes with each facile synthesis procedures and excessive catalytic exercise, providing potential functions in wearable sensors and customized well being monitoring.