In iOS 17, Apple launched a brand new framework known as SwiftData to interchange the Core Information framework. Earlier, now we have written an introductory tutorial about SwiftData and confirmed you how you can pair SwiftData with SwiftUI.
Whereas there are quite a few studying sources out there for utilizing SwiftData with SwiftUI, some readers have talked about that discovering complete guides for integrating SwiftData into UIKit apps will be difficult. On this tutorial, we’ll delve into the method of leveraging the capabilities of SwiftData throughout the UIKit framework.
A Fast Introduction about SwiftData
To begin off, let’s take a short tour of the SwiftData framework. It’s essential to grasp that SwiftData shouldn’t be mistaken for a database itself. As a substitute, it’s a framework constructed upon Core Information, particularly developed to help builders in successfully managing and interacting with knowledge saved persistently. Whereas the default persistent retailer utilized by iOS is usually the SQLite database, it’s value noting that persistent shops can are available in varied types. For example, Core Information can be employed to handle knowledge saved in a neighborhood file, resembling an XML file. This flexibility permits builders to decide on probably the most appropriate persistent retailer for his or her particular necessities.
Whether or not you go for Core Information or the SwiftData framework, each instruments purpose to simplify the intricacies of the underlying persistent retailer for builders. Take the SQLite database, for instance. With SwiftData, there’s no must concern your self with establishing database connections or delving into SQL queries to retrieve knowledge data. As a substitute, builders can give attention to using user-friendly APIs and Swift Macros, resembling @Mannequin, to effectively handle knowledge inside their functions. This abstraction permits for a extra streamlined and intuitive knowledge administration expertise.
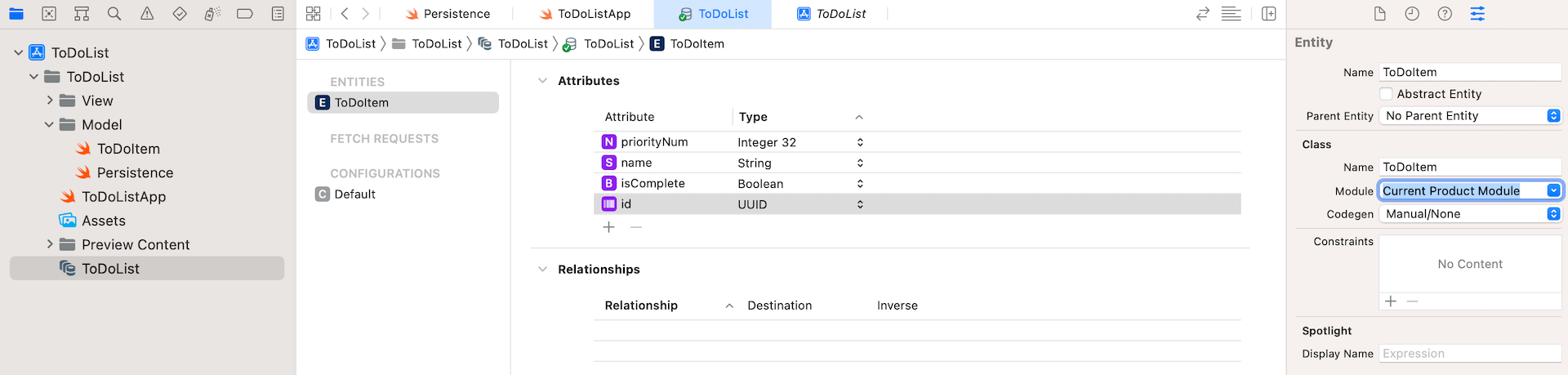
You probably have used Core Information earlier than, you might keep in mind that it’s a must to create a knowledge mannequin (with a file extension .xcdatamodeld) utilizing a knowledge mannequin editor for knowledge persistence. With the discharge of SwiftData, you not want to do this. SwiftData streamlines the entire course of with macros, one other new Swift function in iOS 17. Say, for instance, you already outline a mannequin class for Music as follows:
class Music {
var title: String
var artist: String
var album: String
var style: String
var score: Double
}To make use of SwiftData, the brand new @Mannequin macro is the important thing for storing persistent knowledge utilizing SwiftUI. As a substitute of constructing the information mannequin with mannequin editor, SwiftData simply requires you to annotate the mannequin class with the @Mannequin macro like this:
@Mannequin class Music {
var title: String
var artist: String
var album: String
var style: String
var score: Double
}That is the way you outline the schema of the information mannequin in code. With this easy key phrase, SwiftData mechanically allows persistence for the information class and provides different knowledge administration functionalities resembling iCloud sync. Attributes are inferred from properties and it helps fundamental worth varieties resembling Int and String.
SwiftData permits you to customise how your schema is constructed utilizing property metadata. You possibly can add uniqueness constraints through the use of the @Attribute annotation, and delete propagation guidelines with the @Relationship annotation. If there are particular properties you don’t want included, you should utilize the @Transient macro to inform SwiftData to exclude them. Right here is an instance:
@Mannequin class Album {
@Attribute(.distinctive) var title: String
var artist: String
var style: String
// The cascade relationship instructs SwiftData to delete all
// songs when the album is deleted.
@Attribute(.cascade) var songs: [Song]? = []
}To drive the information persistent operations, there are two key objects of SwiftData that you ought to be acquainted with: ModelContainer and ModelContext. The ModelContainer serves because the persistent backend in your mannequin varieties. To create a ModelContainer, you merely must instantiate an occasion of it.
// Fundamental
let container = attempt ModelContainer(for: [Song.self, Album.self])
// With configuration
let container = attempt ModelContainer(for: [Song.self, Album.self],
configurations: ModelConfiguration(url: URL("path"))))In UIKit, you may instantiate the context for a given mannequin containers like this:
let context = ModelContext(modelContainer)With the context, you’re able to fetch knowledge. You need to use the brand new #Predicate macro to construct predicates. Right here is an instance:
// Specify all of the songs whose style is "Pop"
let songPredicate = #Predicate { $0.style == "pop" } When you outline the standards for fetching, you should utilize the FetchDescriptor and inform the mannequin context to fetch the information.
let descriptor = FetchDescriptor(predicate: songPredicate)
let songs = attempt context.fetch(descriptor) To insert merchandise within the persistent retailer, you may name the insert technique of the mannequin context and cross it the mannequin objects to insert.
modelContext.insert(music)Equally, you may delete the merchandise by way of the mannequin context like this:
modelContext.delete(music)This serves as a short introduction to SwiftData. In case you’re nonetheless feeling uncertain about how you can make the most of SwiftData, there’s no want to fret. You’ll achieve a transparent understanding of its utilization as we’ll construct a easy To-do app utilizing UIKit and SwiftData.
Constructing a Easy To-do App with SwiftData and UIKit
I’ve already developed a fundamental to-do app utilizing UIKit. Nonetheless, the present implementation solely shops the to-do gadgets in reminiscence, which implies the information shouldn’t be persistent. With the intention to handle this limitation, our subsequent step is to switch the app and change from utilizing in-memory arrays to leveraging the ability of SwiftData for storing the to-do gadgets in a database. This enhancement will make sure that the to-do gadgets are saved persistently, permitting customers to entry them even after closing the app.
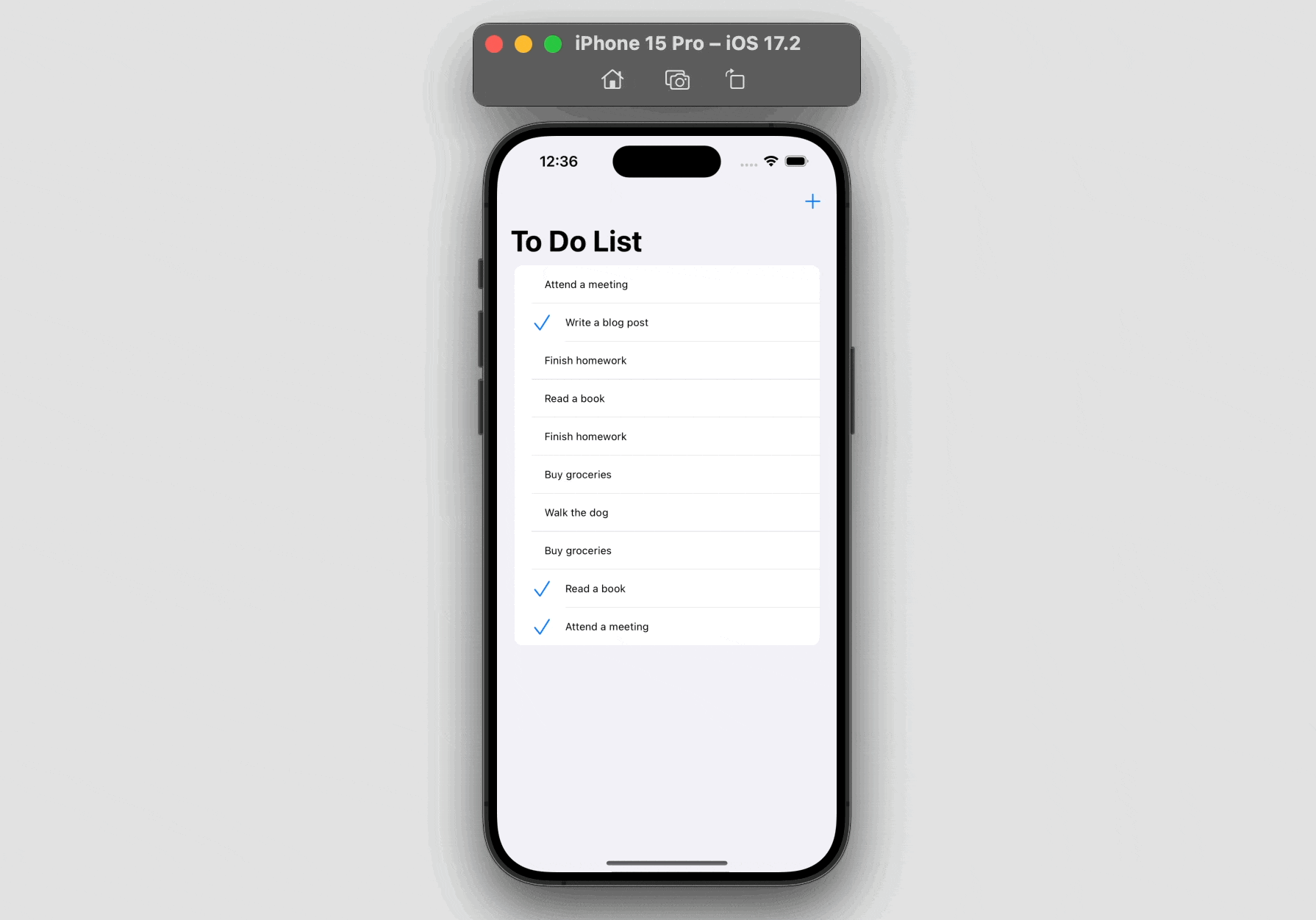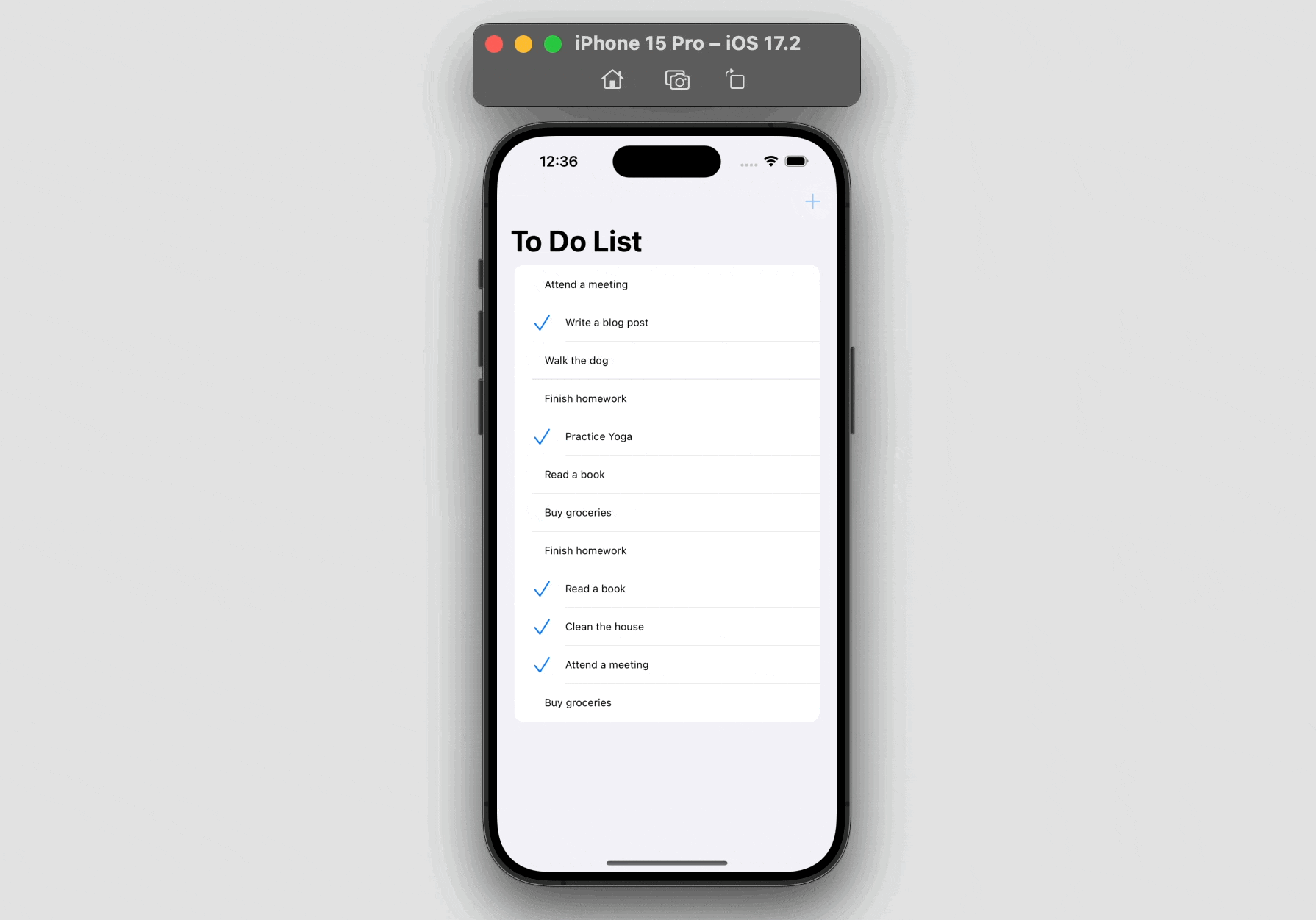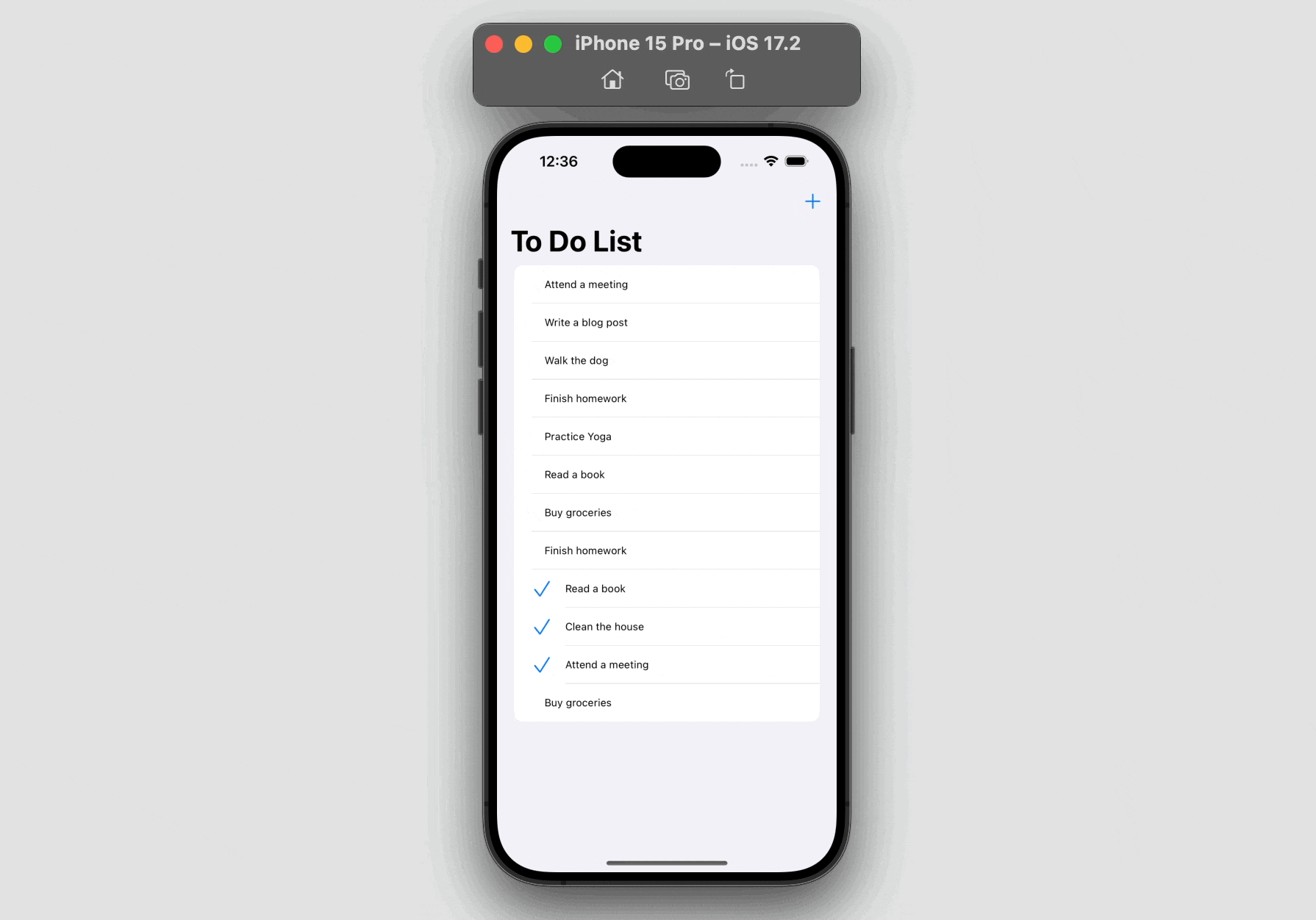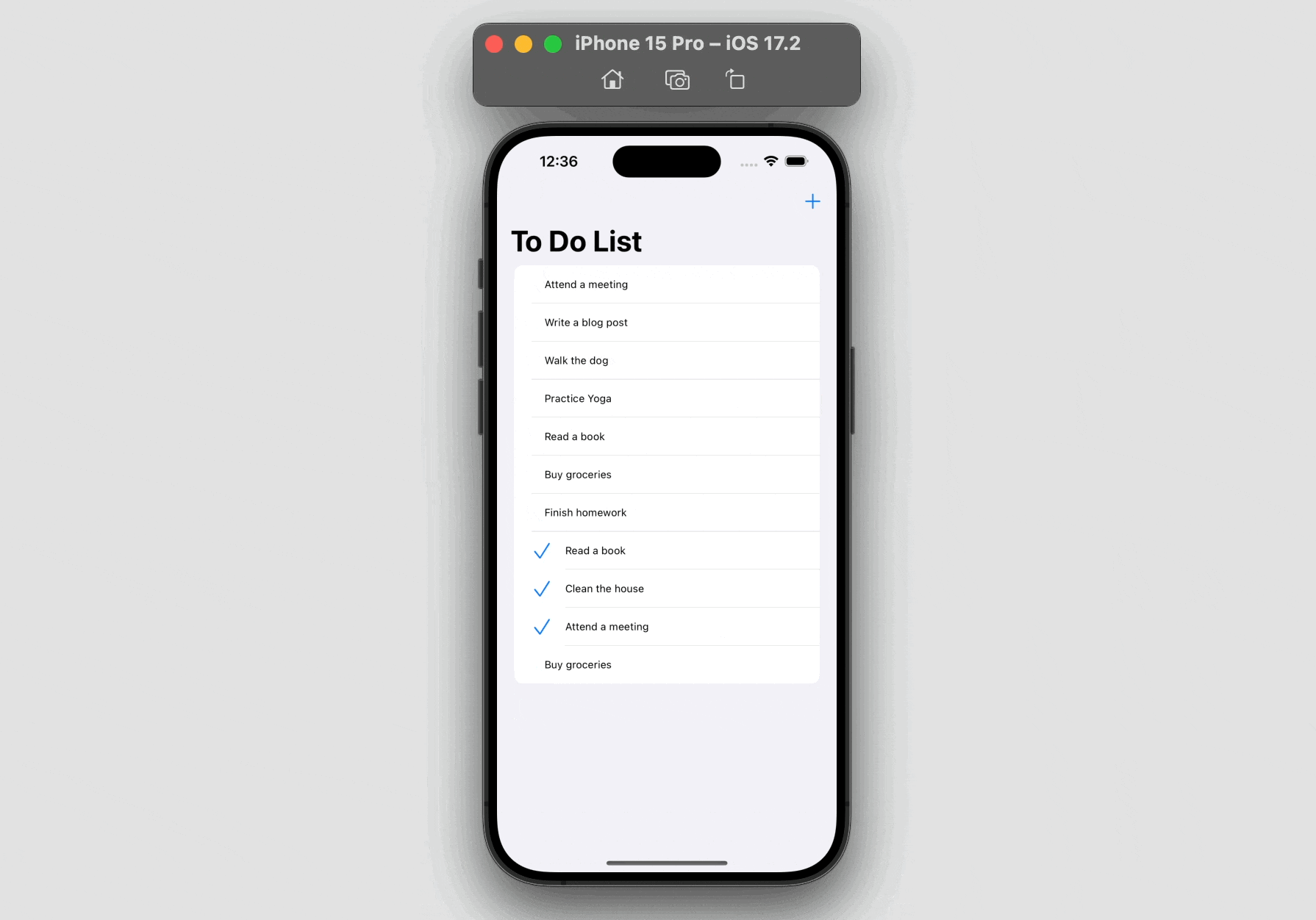
For demo objective, the present model of this app doesn’t present the performance for customers so as to add their very own to-do gadgets. As a substitute, customers can solely add a random to-do merchandise by tapping the “+” button. Nonetheless, customers can nonetheless modify the standing of the prevailing merchandise and delete it by swiping.
Utilizing @Mannequin for the mannequin class
The in-memory model of the app already defines a struct for ToDoItem:
struct ToDoItem: Identifiable, Hashable {
var id: UUID
var title: String
var isComplete: Bool
init(id: UUID = UUID(), title: String = "", isComplete: Bool = false) {
self.id = id
self.title = title
self.isComplete = isComplete
}
}To make use of SwiftData, we are able to convert this struct to class and annotate it with the @Mannequin macro like this:
import SwiftData
@Mannequin class ToDoItem: Identifiable, Hashable {
var id: UUID
var title: String
var isComplete: Bool
init(id: UUID = UUID(), title: String = "", isComplete: Bool = false) {
self.id = id
self.title = title
self.isComplete = isComplete
}
}As you may see, the one factor that we have to do to make a category work with SwiftData is to prefix it with @Mannequin. SwiftData then mechanically allows persistence for the information class.
Saving To-Do Gadgets into Database
Within the demo app, now we have the ToDoTableViewController class to deal with the rendering of the to-do desk view, in addition to, the random creation of the to-do gadgets. To handle knowledge with SwiftData, we first create a variable to carry the mannequin container:
var container: ModelContainer?Within the viewDidLoad technique, we are able to add the next line of code to instantiate the mannequin container:
container = attempt? ModelContainer(for: ToDoItem.self)For including a random to-do merchandise, the demo app already had a technique named addToDoItem:
@IBAction func addToDoItem(sender: UIBarButtonItem) {
todoItems.append(generateRandomTodoItem())
updateSnapshot(animatingChange: true)
}We known as up the generateRandomTodoItem technique to get a to-do merchandise and append it to the todoItems array. Then we name up the updateSnapshot technique to replace the desk view.
With the intention to save the to-do merchandise completely, we are able to change the code like this:
@IBAction func addToDoItem(sender: UIBarButtonItem) {
container?.mainContext.insert(generateRandomTodoItem())
fetchToDoItems()
}As a substitute of merely including the to-do merchandise to the array, we make the most of the insert technique of the container’s context to avoid wasting the merchandise into the interior database.
Fetching Information from Database
The implementation of the fetchToDoItems technique is pending in the intervening time. To retrieve knowledge from the database, we have to create an occasion of FetchDescriptor. This enables us to specify the information sort we wish to retrieve and outline any particular search standards if needed. By using the FetchDescriptor, we are able to successfully retrieve the specified knowledge from the database. After organising the fetch descriptor object, we are able to proceed to name the fetch technique of the container’s context and supply the descriptor as an argument. SwiftData will then make the most of this info to retrieve the to-do gadgets accordingly from the database.
Insert the next code snippet to create the fetchToDoItems technique:
func fetchToDoItems() {
let descriptor = FetchDescriptor()
todoItems = (attempt? container?.mainContext.fetch(descriptor)) ?? []
updateSnapshot()
} As soon as we retrieve all of the to-do gadgets, we have to invoke the updateSnapshot technique to replace the desk view.
Deleting Information from Database
Within the pattern app, now we have a swipe motion for deleting a row merchandise like this:
let deleteAction = UIContextualAction(fashion: .harmful, title: "Delete") { (motion, sourceView, completionHandler) in
var snapshot = self.dataSource.snapshot()
snapshot.deleteItems([todoItem])
self.dataSource.apply(snapshot, animatingDifferences: true)
// Name completion handler to dismiss the motion button
completionHandler(true)
}For now, it solely removes a to-do merchandise from the desk view however not the database. To utterly delete the merchandise from database, we have to insert a line of code within the closure:
self.container?.mainContext.delete(todoItem)By calling the delete technique and offering the related merchandise, SwiftData will care for eradicating the required merchandise from the database, making certain that it’s not continued in our app’s knowledge storage.
That is how we migrate the to-do app from utilizing in-memory storage to database utilizing SwiftData.
Abstract
By following the steps outlined above, we efficiently migrated the to-do app from utilizing in-memory storage to using a database with the assistance of SwiftData. As demonstrated, the mixture of the @Mannequin macro and SwiftData framework simplifies the method of incorporating a database into an app.
We hope that by means of this tutorial, you now possess a clearer understanding of how you can combine SwiftData right into a SwiftUI mission and carry out important CRUD (Create, Learn, Replace, Delete) operations. Apple has invested vital effort in making persistent knowledge administration and knowledge modeling extra accessible for Swift builders, together with newcomers to the language.
With SwiftData, you might have a robust device at your disposal to deal with knowledge storage and retrieval effectively. We encourage you to discover additional and leverage the capabilities of SwiftData to boost your app improvement journey.


