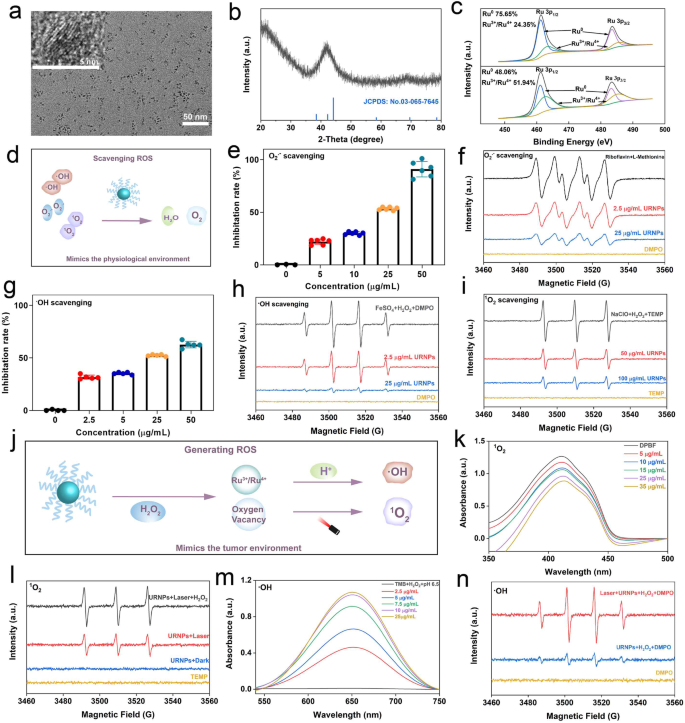
Synthesis and characterization of ultrasmall ruthenium nanoparticles (URNPs)
Uniform URNPs had been synthesized by way of a thermo-decomposition methodology. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) photographs present that the as-prepared merchandise present spherical morphology with a mean diameter of about 2.80 ± 0.50 nm (Fig. 1a and Determine S1). To research the crystal construction of URNPs, we carried out X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses. As proven in Fig. 1b, the attribute peaks which might be just like the everyday ruthenium patterns with hexagonal close-packed (hcp) construction (JCPDS No. 03-065-7645) are noticed in XRD patterns. In keeping with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analyses, the valence of ruthenium in URNPs is predominantly within the type of Ru0, endowing URNPs with excessive reducibility to lower reactive oxygen species (ROS) degree brought on by Cisplatin (DDP) in kidney. We seen a little bit Ru3+/Ru4+ existence in URNPs, which might be ascribed to partial oxidation owing to its ultrasmall measurement. Curiously, the dominant species of Ru change to Ru3+/Ru4+ratio after H2O2 remedy (Fig. 1c). Since ruthenium aspect with excessive valence has been reported as environment friendly chemodynamical remedy (CDT) agent in acidic setting [30], these outcomes indicate that URNPs could act as CDT agent to enhance the efficacy of DDP. With a purpose to switch URNPs into aqueous answer, 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[amino(polyethylene glycol)-2000] has been efficiently modified on its floor. Dynamic gentle scattering (DLS) measurements recognized a hydrodynamic diameter of ~ 8.63 nm and a floor zeta potential of ~ 7.34 mV (Figures S2 and S3), which corresponded to the renal filtration threshold (< 10 nm) for passage by the glomerulus and excretion [31, 32]. Moreover, the steadiness of URNPs was investigated by co-incubating them with deionized distilled water (ddH2O), phosphate buffered saline (PBS), and full medium for 0, 24, and 72 h. It seems that URNPs monodisperse in these media with excessive stability, which is useful to long-term circulation in vivo (Determine S4) (Scheme 1).
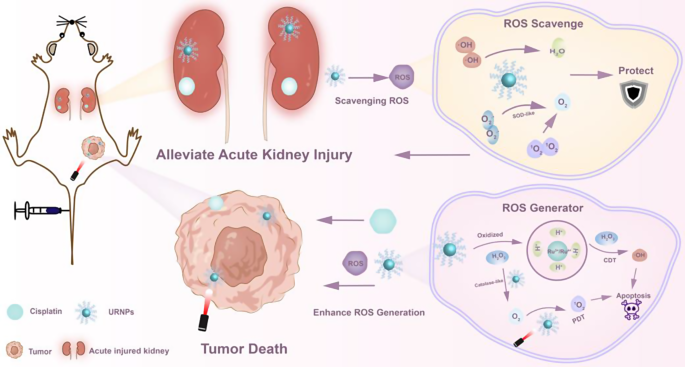
Schematic illustration of URNPs differentially managing ROS degree in tumor and kidney. Within the physiological setting of the kidney, URNPs mimic multi-enzyme actions to guard the kidney by scavenging ROS induced by DDP. In tumor microenvironments, URNPs selectively act as ROS mills to kill tumors that improve the efficacy of DDP
Characterization of URNPs. (a) TEM picture of URNPs, scale bar is 50 nm. Insert is high-resolution TEM picture of URNPs, scale bar is 5 nm. (b) XRD patterns of URNPs. (c) XPS analyses of URNPs earlier than and after oxidizing by H2O2. (d) Schematic illustration of ROS scavenging capability of URNPs in a physiological setting. (e) UV-Vis spectra of O2.− scavenging of URNPs at completely different concentrations within the pH 7.4 answer. (f) ESR spectra analyses of O2.− scavenging of URNPs. (g) UV-Vis spectra of ·OH scavenging of URNPs at completely different concentrations within the pH 7.4 answer. (h) ESR spectra analyses of ·OH scavenging of URNPs. (i) ESR spectra analyses of 1O2 scavenging of URNPs. (j) Schematic illustration of ROS producing of URNPs within the tumor setting. (okay) UV-Vis spectra of 1O2 technology degree within the pH 6.5 answer containing completely different concentrations of URNPs, H2O2, and DPBF below laser irradiation. (l) ESR spectra analyses of 1O2 technology by URNPs in numerous remedies. (m) UV-Vis spectra of ·OH technology degree within the pH 6.5 answer containing completely different concentrations of URNPs, H2O2, and TMB. (n) ESR spectra analyses of ·OH technology degree with URNPs in numerous remedies
ROS scavenging actions of URNPs in impartial physiological setting
As acute kidney harm (AKI) was related to extreme ROS induced by DDP, we assessed the multi-enzyme exercise of URNPs to remove ROS in a simulated impartial physiological setting (Fig. 1d). The SOD-like enzymatic exercise of URNPs was verified by reacting with superoxide anion (O2·−) generated by the irradiation of methionine and riboflavin. The absorption of nitrotetrazolium blue chloride (NBT) at 560 nm is considerably diminished by URNPs (Fig. 1e). Remarkably, URNPs with the focus as little as 50 µg/mL even efficiently remove greater than 91% of the O2·−. In line with the UV-Vis analyses, the electron spin resonance (ESR) spectra verify the concentration-dependent exercise of URNPs as a SOD-like enzyme (Fig. 1f). To discover the scavenging skill of URNPs to hydroxyl radical (·OH), we utilized salicylic acid (SA) as a particular probe to detect the ·OH degree with or with out URNPs within the classical Fenton response system. The attribute sign of ·OH in answer with URNPs is dramatically decrease than that of answer with out URNPs. (Fig. 1g). It ought to observe that the elimination effectivity rises with the rise of URNPs focus, which is additional supported by UV-Vis analyses utilizing methylene blue (MB) as probe (Determine S5). Moreover, we discover that the sign intensities of DMPO/·OH lower with the rise of URNPs focus by ESR spectra (Fig. 1h). We additional verified singlet oxygen (1O2) elimination capability of URNPs by ESR. The ESR spectra outcomes point out that the attribute peaks of two,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMP)/1O2 at presence of URNPs are clearly decrease than that with out URNPs, revealing the scavenging exercise of URNPs to 1O2 (Fig. 1i). These outcomes reveal that URNPs can act as potential antioxidants to remove ROS in a impartial physiological setting based mostly on sturdy multi-enzyme exercise [33].
ROS Era in mimic tumor setting
As antitumor adjuvant, ROS technology of URNPs was stimulated in mimic TME (Fig. 1j) [34]. Since 1O2 has been confirmed to be generated by photosensitizers containing ruthenium [35, 36], we evaluated the feasibility of URNPs to generate 1O2 utilizing 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran (DPBF) as probe. We seen that the sign depth of DPBF decreased at presence of URNPs below 808 nm laser irradiation, whereas no obvious change might be noticed within the group with out URNPs (Determine S6). Moreover, these outcomes present direct proof of URNPs-mediated 1O2 technology in concentration-dependent method (Fig. 1okay). Excitingly, the sign depth of TEMP/1O2 will increase with the introducing of H2O2 in ESR spectra (Fig. 1l). This phenomenon might be ascribed to the CAT-like exercise of URNPs, which catalyze H2O2 into O2 and improve the supply of 1O2 (Determine S7) [37]. To know the mechanism of 1O2 technology by URNPs, we analyzed URNPs by ESR spectra. URNPs exhibit a pointy single electron peak, suggesting the existence of oxygen vacancies (OVs) defects in URNPs (Determine S8). The OVs have been confirmed to supply electron trapping websites to switch electrons to O2 below near-infrared (NIR) laser irradiation [38, 39]. We now have beforehand proved that URNPs might be oxidized by H2O2 and generate Ru3+/4+, which have been thought-about CDT brokers. The capability of the URNPs to generate ·OH was examined utilizing 3,3’,5,5’ -tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) as indicator. It seems that ·OH will be produced even at a low focus of URNPs (2.5 µg/mL) within the presence of H2O2 below an acidic setting, as indicated by the answer altering from colorless to blue (Fig. 1m and Determine S9). Nevertheless, we didn’t observe obvious sign change of TMB with H2O2 at pH 7.4 (Determine S10). ESR spectra analyses additional verify URNPs generate quite a few ·OH in mimic tumor microenvironment (TME), particularly below NIR laser irradiation (Fig. 1n). Notably, the ·OH technology effectivity of URNPs is remarkably elevated below laser irradiation as a result of good photothermal conversion capability, which will increase the temperature and Fenton-like exercise (Determine S11) [40]. The concurrently technology of poisonous 1O2 and ·OH in mimic TME guarantee URNPs to help DDP to kill tumor cells and enhance the efficacy of DDP.
Protecting impact to regular renal cells
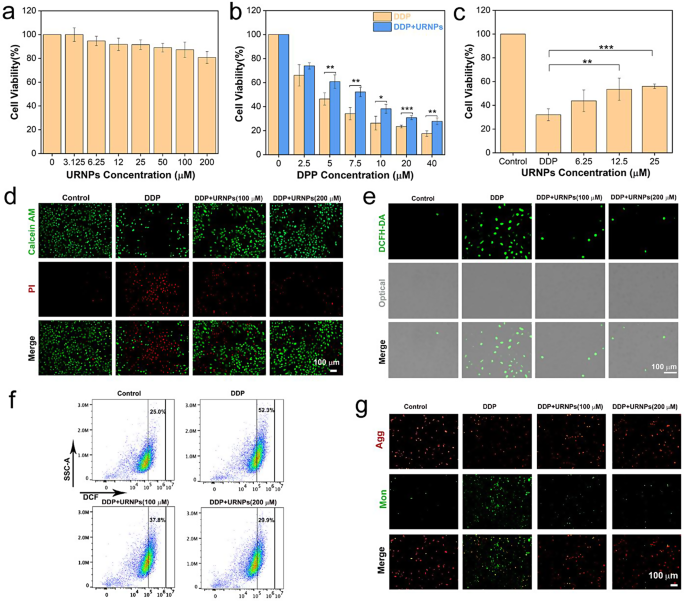
Renal tubules are typical targets for DDP-induced nephrotoxicity and inclined to break by oxidative stress [41]. Consequently, HK-2 cells (human renal tubular epithelial cells) had been chosen as mannequin to analyze the protecting results of URNPs on regular renal cells. Earlier than investigating the protecting impact, we analyzed the cytotoxicity of URNPs to HK-2 cells by cell-counting-kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Of observe, there isn’t a obvious impact of URNPs on the viability of HK-2 cells (Fig. 2a). The excessive biocompatibility motivates us to systematically assess the protecting impact of URNPs on HK-2 cells. We observe notable lower in HK-2 cell survival with incubation of DDP. Curiously, the viability of HK-2 cells handled by DDP considerably elevated after introducing URNPs (Fig. 2b). As well as, the viability improve with the rise of URNPs focus (Fig. 2c). These outcomes clearly reveal the protecting impact of URNPs on HK-2 cells. We additional used double staining of calcein acetoxymethyl ester (calcein-AM) and propidium iodide (PI) to distinguish lifeless from stay cells. It seems that DDP handled cell present evident crimson fluorescence, indicating mass HK-2 cells loss of life. Excitingly, the introducing of URNPs result in dramatic lower of lifeless cells (crimson fluorescence) whereas improve of stay cells (inexperienced fluorescence) (Fig. 2d). These outcomes are extremely in keeping with the CCK-8 assay analyses, demonstrating that URNPs may alleviate DDP-induced cytotoxicity in regular renal cells. Since DDP toxicity has been confirmed to be positively correlated with oxidative stress, we investigated the impact of URNPs on ROS degree in DDP handled HK-2 cells utilizing 2, 7-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) as probe. It seems that the cells handled with DDP present robust inexperienced fluorescence in fluorescence imaging, indicating that DDP will increase the ROS degree in HK-2 cells (Fig. 2e). Notably, the fluorescence depth reveals dramatic lower within the presence of URNPs owing to its ROS scavenging exercise in HK-2 cells (Determine S12). To quantify the fluorescence change, we analyzed the fluorescence of cells handled with completely different situations by circulation cytometry. It seems that the fluorescence depth of DCF within the cells handled by each DDP and URNPs is considerably decrease than that within the cells handled by DDP, demonstrating that URNPs can scale back the oxidative stress of regular renal cells handled by DDP and successfully defend regular renal cells throughout DDP remedy (Fig. 2f). Mitochondrial dysfunction brought on by excessive ROS ranges is likely one of the main causes of DDP-induced nephrotoxicity, leading to a lower in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). Due to this fact, 5,5,6,6-tetrachloro-1,1,3,3-tetraethyl-imidacarbocyanine iodide (JC-1) staining was used to detect mitochondrial membrane potential to additional decide whether or not URNPs suppress DDP-induced cytotoxicity. The strongest inexperienced fluorescence is noticed within the cells handled by DDP, whereas we observe important improve in crimson fluorescence (mixture) and reduce in inexperienced fluorescent (monomer) after introducing URNPs (Fig. 2g). These outcomes counsel that URNPs defend the mitochondria from ROS harm in regular renal cells.
Protecting impact on regular renal cells. (a) The cell viability of HK-2 cells after remedy with completely different concentrations of URNPs. (b) The cell viability of HK-2 cells after remedy with 100 µM URNPs and completely different concentrations of DDP. P(5 µM) = 0.0092, P(7.5 µM) = 0.0014, P(10 µM) = 0.0124, P(20 µM) = 0.0004, P(40 μM) = 0.0011.(c) The cell viability of HK-2 cells after remedy with 7.5 µM DDP and completely different concentrations of URNPs. P(12.5 µM) = 0.0014, P(25 µM) = 0.0004. (d) Stay/lifeless cell staining assessments of HK-2 cells after remedy with 7.5 µM DDP and completely different concentrations of URNPs. Pink, lifeless cells; inexperienced, stay cells. Scale bar is 100 μm. (e) Fluorescence photographs of HK-2 cells after completely different remedies to watch ROS through the use of DCFH-DA as an indicator. Scale bar is 100 μm. (f) The DCF fluorescence depth is quantified by way of circulation cytometry. (g) Fluorescence photographs of HK-2 cells after completely different remedies to detect mitochondrial membrane potential measurement by JC-1 probes. Scale bar is 100 μm. (The 2 teams had been analyzed utilizing Pupil’s t-test; between three or extra teams utilizing one-way ANOVA with a number of comparisons take a look at. n = 4, imply ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001)
Enhancing the efficacy of DDP to tumor cells
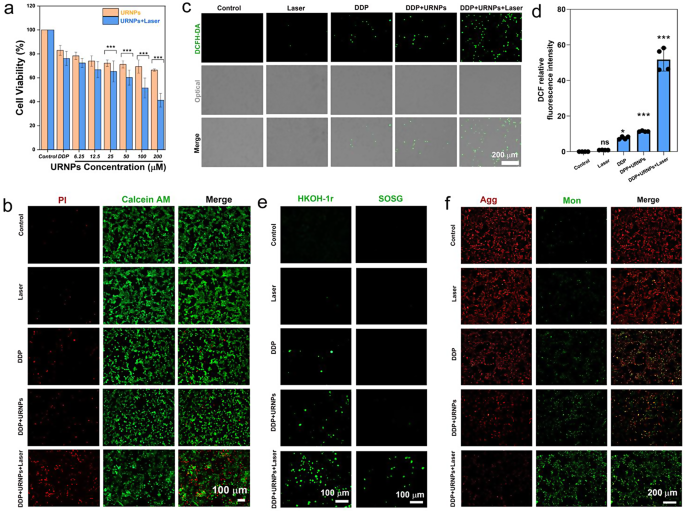
Since URNPs have beforehand been confirmed to generate ample ROS in mimic TME below laser irradiation, we investigated whether or not URNPs may act as adjuvant to enhance the efficacy of DDP. We selected mouse breast most cancers (4T1) cells as a mannequin resulting from the truth that DDP was generally employed to deal with breast most cancers in clinic. CCK-8 evaluation point out that URNPs reveals outstanding tumor cell suppression (Determine S13). By monitoring intracellular ROS ranges, ROS had been generated by URNPs, together with ·OH. Because of the elevated oxidative stress brought on by URNPs in tumor cells, the mitochondrial membrane potential decreases. Broken mitochondria activate cell apoptosis, potentiating tumor remedy therapeutic outcomes (Determine S14) [42]. Moreover, ROS mediated by CDT or PDT can induce pyroptosis in tumor cells [43, 44]. It’s speculated that ROS generated by URNPs may induce pyroptosis in tumor cells. Thus, the mechanism of adjuvant chemotherapy with URNPs is to synergistically induce apoptosis and pyroptosis by producing ROS. Primarily based on the a number of programmed cell loss of life induced by URNPs, which can be utilized to boost the efficacy of DDP in tumor remedy. These outcomes motivated us to additional consider the impact of URNPs on the efficacy of DDP to tumor cells. It seems that introducing URNPs barely will increase the tumor-killing effectivity of DDP (Fig. 4a). We observe that the tumor suppression effectivity might be additional elevated by introducing close to infrared (NIR) laser as a result of technology of 1O2 by URNPs below laser irradiation (Determine S13). The cell viability of cells handled by DDP and 200 µM URNPs below laser irradiation decreased to 41.3%, which is considerably decrease than cells handled by DDP alone (82.9%). Nevertheless, no obvious impact of laser on the cell viability of tumor cells handled by DDP is noticed. AM/PI co-staining analyses point out that tumor cells handled by URNPs and DDP present stronger crimson fluorescence (lifeless cells) whereas weaker inexperienced fluorescence (stay cells) in comparison with that handled by DDP alone, demonstrating the elevated tumor killing effectivity brought on by URNPs (Fig. 3b). We additional analyzed the ROS degree of 4T1 cells with completely different remedies. As anticipated, the introducing of URNPs will increase the depth of inexperienced fluorescence in DDP-treated cells, particularly below laser irradiation (Fig. 3c, d). These outcomes point out that URNPs considerably improve the oxidative stress of tumor cells throughout DDP remedy. To reveal the simultaneous technology of ·OH and 1O2 by URNPs, we selected HKON-1r and SOSG as probes to watch the ·OH and 1O2 ranges. We observe that tumor cells handled by URNPs and DDP present considerably stronger fluorescence than cells handled by DDP in HKON-1r staining, suggesting the improved ·OH degree brought on by URNPs by Fenton-like response (Fig. 3e). Furthermore, the extreme inexperienced fluorescence might be solely famous in cells handled by URNPs and DDP below laser irradiation in SOSG staining, confirming the profitable technology of 1O2 by URNPs. Moreover, we detected mitochondrial membrane potential adjustments in 4T1 tumor cells by JC-1 to evaluate the mitochondrial dysfunction brought on by elevated oxidative stress. As anticipated, the strongest inexperienced fluorescence is noticed within the DDP + URNPs + Laser group, suggesting that URNPs considerably reduces the mitochondrial membrane potential and induces quite a few cells to bear early apoptosis (Fig. 3f). These outcomes reveal that URNPs efficiently swap to ROS technology in TME and acts as promising DDP adjuvant for subsequent tumor remedy.
URNPs enhance the efficacy of DDP to tumor cells. (a) The cell viability of 4T1 cells after remedy by 5 µM DDP and completely different concentrations of URNPs with or with out laser irradiation. P(25 µM);P(50 µM);P(100 µM);P(200 µM) < 0.001. (b) Stay/lifeless cell staining assessments of 4T1 cells handled by saline, Laser, DDP, DDP + URNPs, and DDP + URNPs + Laser. Pink, lifeless cells; inexperienced, stay cells. Scale bar is 100 μm. (c) Fluorescence photographs of cells below completely different remedies to watch ROS through the use of DCFH-DA as an indicator. Scale bar is 200 μm. (d) Quantitative DCF fluorescence depth analyses of ROS technology. P(Laser) = 0.9915, P(DDP) = 0.014, P(DDP + URNPs) = 0.0005, P(DDP + URNPs +Laser) < 0.0001. (e) The intracellular ·OH and 1O2 had been detected by HKON-1r and SOSG probes as fluorescence probes below completely different remedies. Scale bar is 100 μm. (f) Fluorescence photographs of cells below completely different remedies to watch mitochondrial membrane potential measurement by JC-1 probes. Scale bar is 200 μm. (The 2 teams had been analyzed utilizing Pupil’s t-test; between three or extra teams utilizing one-way ANOVA with a number of comparisons take a look at. n = 4, imply ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001)
In vivo biocompatibility and biodistribution of URNPs
To evaluate the biosafety of URNPs, we carried out a hemolysis take a look at. The hemolysis fee of URNPs (400 µM) was lower than 5%, indicating excessive biosafety of URNPs (Determine S15). To additional examine in vivo toxicity, we intravenously injected URNPs (3 mg/kg) into wholesome mice and picked up blood samples to research the liver and renal perform. The blood biochemical indexes, together with aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and creatinine (CREA) are inside the regular degree. In the meantime, the blood routine analyses present no important distinction between the URNPs-treated group and the saline-treated group (Determine S16). These outcomes reveal the excessive biocompatibility of URNPs, making them splendid choices for medical DDP adjuvants that may be utilized for subsequent remedy. To verify the URNPs had been focused to the organ website, we performed ICP-MS evaluation, to quantify the quantity of Ru ions in numerous organs and tumor. The outcomes confirmed that URNPs may quickly attain kidneys and tumors inside 1 h with accumulation charges of 4.38percentID/g and 1.05percentID/g(Determine S17). It seems that URNPs successfully collected within the tumor website by way of the improved permeability and retention (EPR) impact. In the meantime, URNPs can successfully accumulate in kidney, owing to their small measurement. Moreover, the buildup quantity is decreased with the time extension (Determine S18). Contemplating the advantages of tumor progress inhibition and balancing the therapeutic impact of URNPs on kidneys, we selected to deal with the tumor with a laser 1 h after injection of URNPs.
URNPs alleviate DDP-induced AKI in vivo
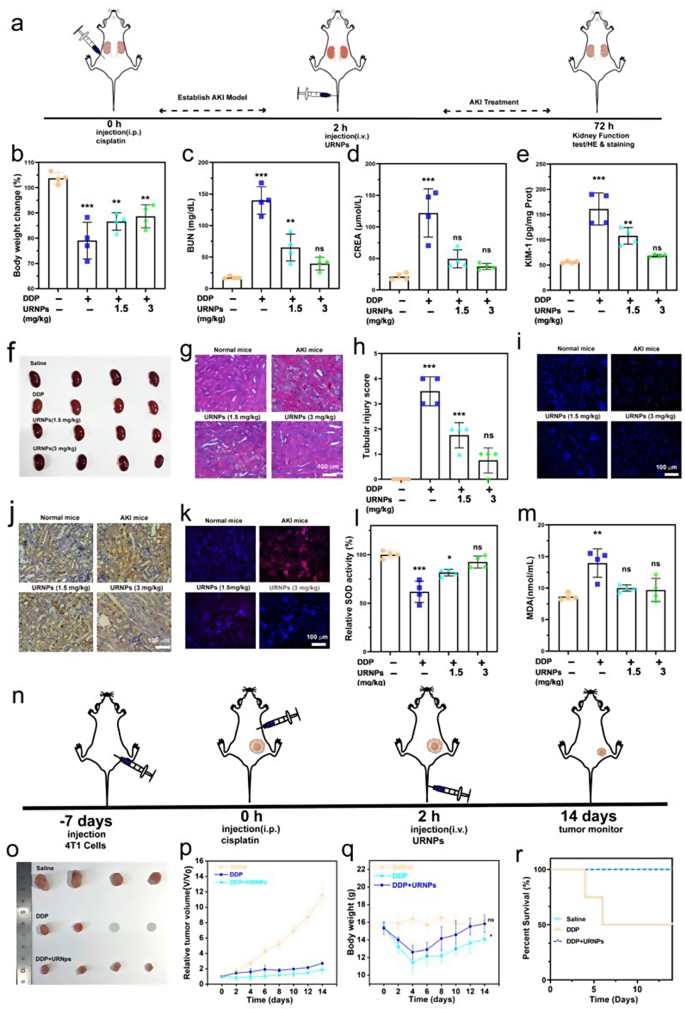
AKI mice fashions had been established by intraperitoneal injection of DDP with the dosage of 15 mg/kg into wholesome mice. We observe important weight reduction in saline-treated AKI mice, whereas the AKI mice handled by URNPs present comparable weight to wholesome mice (Fig. 4b). Furthermore, it seems that the AKI mice handled by saline present larger nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine (CREA) ranges in comparison with wholesome mice, indicating irregular renal perform in AKI mice (Fig. 4c and d). The BUN and CREA ranges lower to the traditional degree with the help of URNPs, demonstrating the restoration of renal perform. Moreover, the expression of kidney harm molecule-1 (KIM-1) was analyzed. The saline handled AKI mice present considerably larger ranges of KIM-1 in comparison with URNPs handled mice, which is analogous to wholesome mice (Fig. 4e). These outcomes point out the reduction impact of URNPs on renal harm. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of renal tissues from saline-treated AKI mice present extreme renal harm, as evidenced by quite a few casts, dilated, and necrotic tubules (Fig. 4g). Nevertheless, URNPs handled AKI mice exhibit the everyday construction of renal tubular. To quantify the diploma of renal harm, we calculated the tubular harm rating based mostly on the H&E staining (Fig. 4h) [16]. It seems that the rating of saline handled AKI mice is clearly larger than the wholesome mice and URNPs handled AKI mice, demonstrating the alleviation impact of URNPs on AKI. These outcomes are strongly supported by TUNEL fluorescence staining and immunohistochemical 3,3’-diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining analyses on renal tissues (Fig. 4i and j). Each TUNEL and DAB staining photographs point out that the sign intensities in saline-treated AKI mice are considerably larger than that in URNPs-treated AKI mice. Particularly, the apoptosis ratios of renal cells are decreased with the rise of URNPs focus. To know the connection between ROS scavenging of URNPs and its alleviation impact on AKI, we measure the extent of ROS within the kidney tissue by staining the kidney tissue with dihydroethidium (DHE). The renal tissues of the URNPs handled AKI mice present dramatically decrease ROS degree in comparison with the saline-treated one, immediately revealing ROS scavenging of URNPs within the renal tissue (Fig. 4okay). Since superoxide dismutase (SOD) performed an vital function within the elimination of extra ROS, we additional measured the degrees of the SOD and malondialdehyde (MDA) in kidney tissue The SOD degree of saline handled AKI mice is considerably decrease than that of URNPs handled AKI mice, proving the restoration of SOD brought on by URNPs (Fig. 4l). Quite the opposite, the introducing of URNPs result in the elevated MDA degree brought on by DDP return to the traditional degree (Fig. 4m).
URNPs alleviate DDP-induced AKI in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of AKI mice mannequin institution and remedy. The mice in 4 teams had been handled with: saline, DDP (15 mg/kg), DDP (15 mg/kg) + URNPs (1.5 mg/kg), and DDP (15 mg/kg) + URNPs (3 mg/kg) (n = 4). (b) adjustments in physique weight of mice with completely different remedies. P(DDP) < 0.0001, P(1.5 URNPs) = 0.0013, P(3 URNPs) = 0.0037. (c) BUN. P(DDP) < 0.0001, P(1.5 URNPs) = 0.0059, P(3 URNPs) = 0.2568; and (d) CREA ranges in sera of mice after completely different remedies. P(DDP) < 0.0001, P(1.5 URNPs) = 0.0069, P(3 URNPs) = 0.7805. (e) KIM-1 ranges in renal homogenates. P(DDP) < 0.0001, P(1.5 URNPs) = 0.3034, P(3 URNPs) = 0.7533. (f) Optical images of kidney. (g) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of kidney tissues from completely different group. Scale bar is 100 μm. (h) The tubular harm scores that had been calculated in line with the share of broken tubules from H&E sections. P(DDP) < 0.0001, P(1.5 URNPs) = 0.0008, P(3 URNPs) = 0.1469. (i) Fluorescence photographs of kidney tissues had been collected from completely different teams stained by DAPI (blue fluorescence) and TUNEL (inexperienced fluorescence). Scale bar is 100 μm. (j) DAB staining of kidney tissues in numerous teams. The size bar is 100 μm. (okay) Fluorescence photographs of kidney tissues collected from completely different teams stained by DHE (crimson fluorescence) and DAPI (blue fluorescence). The size bar is 100 μm. (l) SOD P(DDP) < 0.0001, P(1.5 URNPs) = 0.0107, P(3 URNPs) = 0.4314. (m) MDA ranges in numerous teams. P(DDP) = 0.0015, P(1.5 URNPs) = 0.5872, P(3 URNPs) = 0.7514. (n) The tumor-bearing mice had been divided into three teams: saline, DDP (6 mg/kg), DDP (6 mg/kg) + URNPs (3 mg/kg). Schematic illustration of tumor-bearing mice mannequin institution and remedy. (o)The optical photographs of tumors in numerous teams. (p) Relative tumor quantity of mice in numerous teams. (q) Physique weight adjustments of mice with completely different remedies. P(DDP) = 0.018, P(DDP + URNPs) = 0.6712. (r) The survival likelihood of mice in numerous teams. (The teams had been analyzed utilizing one-way ANOVA with a number of comparisons take a look at. n = 4, imply ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001)
It was discovered that an AKI mice mannequin obtained by administering a single excessive dose of DDP was incompatible with tumor sufferers’ doses. Most most cancers sufferers handled with cisplatin within the clinic obtain low-dose cisplatin to attenuate the danger of nephrotoxicity and maximize antitumor effectiveness. Sufferers receiving cisplatin for stable tumor remedy are usually given it chronically at a dose of lower than 10 mg/kg [45]. Motivated by the AKI alleviation exercise of URNPs, we verified whether or not URNPs may work as a DDP adjuvant to alleviate AKI throughout high-dosage DDP remedy. Thus, we selected a single intraperitoneal injection of 6 mg/kg of DDP (Fig. 4n). Particularly, 4T1 tumor-bearing BALB/c mice had been randomly divided into three teams: Saline, DDP, and DDP + URNPs. In contrast with the saline group, tumor progress is markedly inhibited within the DDP and DDP + URNPs group, owing to the excessive dosage DDP based mostly anti-tumor efficacy. It ought to observe that the tumor suppression impact of the DDP + URNPs group is barely larger than that within the DDP group as a result of delicate CDT impact of URNPs (Fig. 4o, p, and Determine S19). Though high-dosage DDP successfully inhibits the expansion of tumors, it leads to an apparent lower in physique weight and even results in the loss of life of handled mice (Fig. 4q and r). Additional, H&E staining of surviving mice revealed that DDP handled mice had renal tubular harm, together with tubular dilation, lack of brush border, and epithelial degeneration (Determine S20). Excitingly, there aren’t any obvious variations within the physique weight and renal construction of the DDP + URNPs group in comparison with wholesome mice. Extra importantly, all mice handled with high-dosage DDP utilizing URNPs as adjuvant are alive in the course of the remedy with excessive therapeutic efficacy, suggesting that URNPs work as environment friendly adjuvant to alleviate DDP-induced AKI with improved efficacy.
URNPs enhance efficacy of DDP in low dosage
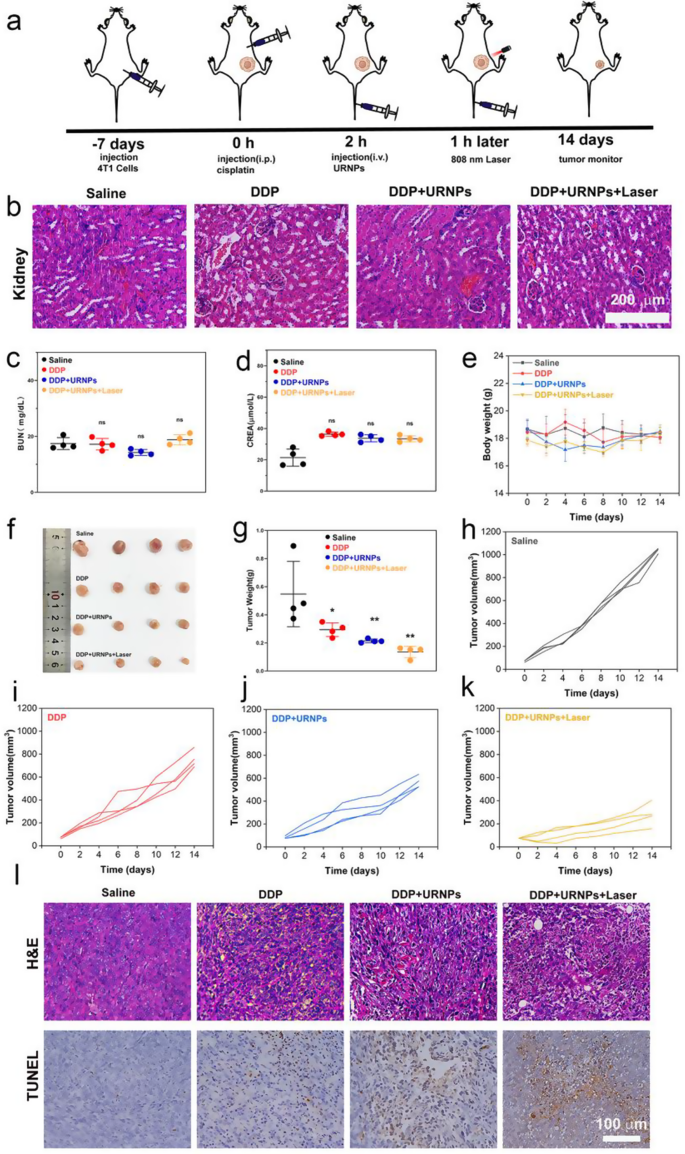
Though DDP at 6 mg/kg seems to be an efficient most cancers remedy in vivo experiments with tumor-bearing mice, it additionally results in inevitable renal toxicity and mortality. The purpose of DDP remedy is to kill the most cancers, thus prolonging the affected person’s life. With a purpose to maximize the interpretation of experimental progress into medical use, we elevated the frequency of DDP use and decreased the dose to imitate medical administration. Due to this fact, DDP doses of three mg/kg as soon as every week had been chosen (Fig. 5a). 4 teams of 4T1 tumor-bearing mice had been chosen: Saline, DDP, DDP + URNPs, and DDP + URNPs + Laser. We famous that each one mice present typical renal tubular constructions with none harm (Fig. 5b). Moreover, the BUN and CREA ranges in all teams are just like management group, indicating the restricted impact of low DDP dosage on renal perform (Fig. 5c and d). It ought to observe that no obvious adjustments in physique weight in the course of the 14-day remedy interval (Fig. 5e). These outcomes reveal that discount of DDP dosage can successfully restrict the prevalence of AKI. Sadly, the inhibition of DDP on tumor progress are considerably diminished. In comparison with the mice handled by DDP, the tumor progress of mice handled by each DDP and URNPs is markedly inhibited (Fig. 5f-k and Determine S21). The inhibition fee in DDP + URNPs and DDP + URNPs + laser group elevated from 27.76% (DDP group) to 52.67% and 74.77% (Determine S22). To additional assess the therapeutic results of assorted remedies, tumors from completely different teams are excised for H&E and TUNEL staining. Regardless of evident cell apoptosis/loss of life within the DDP group, the best tumor cell necrosis ratio occurred within the DDP + URNPs + Laser group (Fig. 5l). This phenomenon might be attributed to the improved oxidative stress induced by the URNPs-based ROS technology in tumors. With a purpose to show this hypothesis, we additional handled tumor bearing mice by URNPs. The DHE staining of tumor tissues handled by URNPs point out that URNPs may efficiently mediate ROS technology in vivo, particularly below laser irradiation. In the meantime, TUNEL staining photographs reveal a lot of apoptotic cells, confirming that URNPs could enhance DDP tumor efficacy by way of ROS manufacturing to induce cell apoptosis. The tumor progress of mice handled by URNPs are successfully inhibited as a result of efficient CDT and PDT of URNPs (Determine S23 and S24). Thus, it’s a sensible method to help DDP efficacy by inducing apoptosis by URNPs producing ROS in vivo. Moreover, we don’t observe any histopathological abnormalities within the main organs in all teams, indicating negligible adversarial results of URNPs on the mice (Determine S25 and S26). These outcomes point out the numerous potential of URNPs with CDT/PDT synergy remedy exercise to enhance anti-tumor efficacy of DDP with excessive biocompatibility. Motivated by the low dose of three mg/kg of unhazardous DDP as soon as every week, we selected to proceed to extend the frequency of administration. To additional consider whether or not URNPs may defend the kidneys from cisplatin nephrotoxicity, DDP doses of three mg/kg twice every week had been chosen. We observe that URNPs remedy efficiently improves the survival of mice handled by DDP with excessive dosage (Determine S27).
Fig. 5
URNPs enhance efficacy of DDP in security dosage. (a) Schematic illustration of 4T1 tumor-bearing mice mannequin institution and remedy. The mice in 4 teams had been handled with: saline, DDP (3 mg/kg), DDP (3 mg/kg) + URNPs (3 mg/kg), and DDP (3 mg/kg) + URNPs (3 mg/kg) + Laser (0.47 w/cm2) (n = 4). (b) H&E staining of kidney tissues from completely different teams. (c) BUN P(DDP) = 0.9982, P(DDP + URNPs) = 0.1127, P(DDP + URNPs +Laser) = 0.7133. (d) CREA ranges of mice after the remedies. P(DDP) = 0.5978, P(DDP + URNPs) = 0.7051, P(DDP + URNPs +Laser) = 0.6578. (e) Physique weight adjustments of mice with completely different remedies (f) {Photograph} of tumors after remedies on day 14 (n = 4). (g) Weight of tumors collected from tumor-bearing mice. P(DDP) = 0.05, P(DDP + URNPs) = 0.0098, P(DDP + URNPs +Laser) = 0.002. Tumor progress curves of mice within the teams of (h) saline, (i) DDP, (j) DDP + URNPs, and (okay) DDP + URNPs + Laser. (l) H&E and TUNEL staining of tumor tissues from completely different teams. Scale bar is 100 μm. (The teams had been analyzed utilizing one-way ANOVA with a number of comparisons take a look at. n = 4, imply ± SD, *p < 0.05, and **p < 0.01)