Blockchain expertise is a decentralized, distributed ledger that securely information the possession of digital belongings. The information saved on a blockchain is immutable, making the expertise a major disruptor in industries akin to funds, cybersecurity, and healthcare.
As an immutable digital ledger, blockchain allows safe transactions throughout a peer-to-peer community. It makes use of decentralized strategies to file, retailer, and confirm information, eradicating the necessity for intermediaries akin to banks or governments. Each transaction is documented and saved inside a block on the blockchain. These blocks are encrypted for cover and linked to the previous block, forming a chronological chain—therefore the title “blockchain.” With out the consensus of the community, the information saved on a blockchain can’t be altered or deleted. This new-age database acts as a single supply of reality and facilitates trustless and clear information change amongst interconnected computer systems.
Past transferring cryptocurrencies between wallets, blockchain expertise holds wide-ranging software potential. It could actually assist stop fraudulent banking actions, alleviate provide chain bottlenecks, and safeguard medical information. Blockchain, as a sophisticated database system, facilitates clear data sharing throughout a enterprise community. The information is saved in blocks linked collectively in a chronological chain, making certain that it can’t be deleted or modified with out community consensus. This functionality makes blockchain expertise good for establishing an unchangeable ledger to trace orders, funds, accounts, and varied different transactions. Constructed-in mechanisms stop unauthorized entries, making certain consistency within the shared view of transactions.
Blockchain serves as a shared, immutable ledger that information transactions and tracks belongings inside a enterprise community. Property will be tangible, like homes, vehicles, money, and land, or intangible, akin to mental property, patents, copyrights, and branding. By monitoring and buying and selling just about something of worth on a blockchain community, the expertise reduces threat and cuts prices for all contributors.
Blockchain: Understanding Its Core Mechanisms in 4 Steps
Blockchains are distributed data-management techniques that file each change between customers. These immutable digital information make use of varied strategies to ascertain a trustful system that operates with out intermediaries.
Every block accommodates saved information and a novel alphanumeric code known as a hash, which acts as a digital fingerprint. Blocks are linked collectively utilizing these hashes, making a chronological sequence and offering tamper-proofing. Any alteration within the hash generates a special string, making it simple to identify and reject invalid blocks.
Decentralization is one other essential side of blockchain. As a substitute of a government, management is distributed throughout a peer-to-peer community of interconnected computer systems, or nodes. These nodes continually talk to maintain the digital ledger up to date. Throughout transactions, all nodes take part in validating the transaction utilizing consensus mechanisms. Constructed-in protocols guarantee all nodes agree on a single information set, and blocks can solely be added as soon as verified and consensus is reached. Sensible contracts, that are self-executing packages coded into the blockchain, have streamlined this verification course of.
As soon as recorded, transactions are everlasting, as blockchains don’t enable reversible actions This immutability promotes transparency all through the community and ensures a dependable file of all blockchain actions.
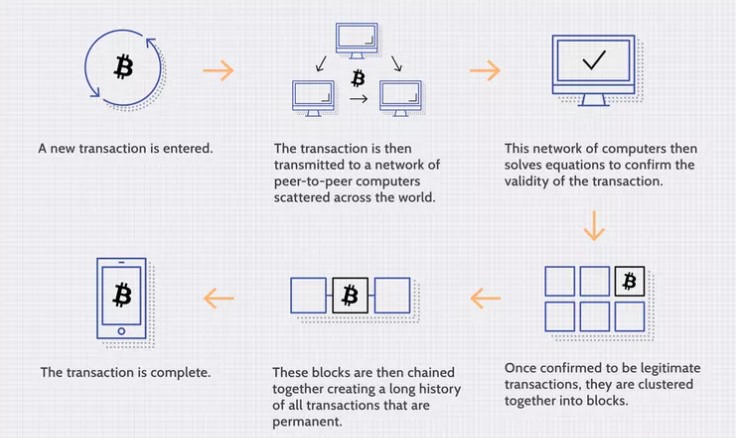
Blockchain expertise, whereas advanced, will be damaged down into 4 fundamental steps, usually automated by blockchain software program:
Step 1 – As every transaction happens, it’s recorded as a “block” of knowledge:
A blockchain transaction information the change of bodily or digital belongings between events throughout the community. This transaction is recorded as an information block, detailing who was concerned, what occurred, when and the place it occurred, why it passed off, the amount of the asset exchanged, and the pre-conditions met through the transaction.
Step 2 – Achieve consensus:
To be deemed legitimate, a transaction should obtain consensus from the vast majority of contributors within the blockchain community. The foundations for attaining consensus are sometimes established on the community’s inception and might fluctuate relying on the community sort.
Step 3 – Hyperlink the blocks:
As soon as consensus is achieved, the transaction is added to a block, akin to a web page in a ledger. Every block features a cryptographic hash, which hyperlinks it to the earlier block, forming a sequence. Any alteration within the block’s contents modifications the hash worth, enabling simple detection of tampering. This chaining course of securely hyperlinks blocks, making them immutable and strengthening the verification of earlier blocks and the complete blockchain.
Step 4 – Share the ledger:
The up to date central ledger is distributed to all contributors within the community, making certain everybody has the most recent copy.
Varieties of Blockchain Networks
- Public Blockchain
Public blockchains are totally open and decentralized, permitting anybody with web entry and a pc to take part. These permissionless networks grant all contributors equal rights to learn, edit, and validate the blockchain. Frequent makes use of embrace cryptocurrency exchanges and mining, with notable examples being Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin.
- Personal Blockchain
In distinction, personal blockchains are extra centralized and managed by a single group, making them safer. These managed blockchains prohibit entry, permitting solely chosen nodes to take part. Examples embrace Ripple, a digital foreign money change community for companies. Key traits are:
– Restricted entry in comparison with public blockchains.
– Out there solely to approved customers.
– Operated inside a closed community.
– Participation restricted to particular members of a company.
- Hybrid Blockchain
Hybrid blockchains combine options of each personal and public blockchains. Organizations can management sure elements whereas making others publicly accessible. This setup makes use of good contracts to permit public verification of personal transactions. For instance, a hybrid blockchain may allow public entry to digital currencies whereas retaining bank-owned foreign money information personal. Options embrace:
– Integration of private and non-private blockchains.
– Utilization of each permission-based and permissionless techniques.
– Person entry managed by way of good contracts.
– Main entities can’t alter transactions regardless of possession.
- Consortium Blockchain
Consortium blockchains, or federated blockchains, are ruled by a number of preselected organizations that share accountability for sustaining the blockchain and setting entry permissions. This sort is well-suited for industries with widespread goals, just like the International Transport Enterprise Community Consortium, which seeks to digitize the delivery business and enhance cooperation amongst maritime operators. Key facets embrace:
– A collaborative answer managed by a number of organizations.
– Mixture of private and non-private blockchain options.
– Shared governance and accountability.
Blockchain Transforms Industries: From Banking to Provide Chain Integrity
Blockchain expertise is being utilized in varied industries past cryptocurrencies. Notably, it affords a safe and environment friendly option to retailer information and observe transactions. Corporations like Walmart, Pfizer, AIG, Siemens, and Unilever are experimenting with blockchain. As an example, IBM’s Meals Belief blockchain traces meals merchandise to make sure security by shortly figuring out contamination sources, thereby stopping widespread foodborne sicknesses.
Within the banking sector, blockchain can revolutionize transaction processing by offering quicker and safer fund transfers, decreasing the time and threat related to conventional banking operations. For inventory buying and selling, it may possibly expedite the settlement course of, slicing down the time taken to clear trades.
In healthcare, blockchain can securely retailer medical information, making certain they’re tamper-proof and accessible solely to approved people. Property information can profit by transferring from inefficient, error-prone guide processes to a safe, immutable digital ledger, which is especially helpful in areas with weak governmental infrastructure.
Sensible contracts, powered by blockchain, facilitate automated transactions when predefined circumstances are met. In provide chains, blockchain enhances transparency by monitoring the origin and journey of merchandise, validating claims like “Natural” and “Honest Commerce.”
The expertise additionally has potential functions in voting techniques, enhancing safety and transparency whereas decreasing fraud and growing voter turnout. Within the power sector, blockchain facilitates peer-to-peer power buying and selling and allows crowdfunding for renewable power initiatives.
Finance makes use of blockchain to streamline on-line funds, account administration, and market buying and selling. For instance, Singapore Change Restricted employs blockchain for extra environment friendly interbank funds. In media and leisure, blockchain improves copyright information administration, making certain honest compensation for artists and decreasing prices. Retail firms, like Amazon, are utilizing blockchain to confirm the authenticity of products of their provide chains, making certain belief within the merchandise offered.
Bitcoin vs. Blockchain: Distinct Ideas with Broad Expertise Purposes
Bitcoin and blockchain are sometimes used interchangeably, however they’re distinct ideas. Bitcoin was one of many first functions of blockchain expertise, resulting in some confusion. Nonetheless, blockchain has many makes use of past Bitcoin.
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital foreign money designed for on-line monetary transactions. It’s now considered a digital asset that may be transformed into varied international currencies like USD or euros. Bitcoin transactions are managed by a public blockchain community that maintains a central ledger.
The Bitcoin community operates by means of a public ledger that information all transactions. Servers worldwide, often called nodes, maintain copies of this ledger, functioning equally to banks. Not like conventional banks, which solely observe their prospects’ transactions, Bitcoin nodes are conscious of each Bitcoin transaction globally.
Anybody can arrange a node with a spare pc, successfully creating their very own Bitcoin financial institution.
Within the Bitcoin community, cryptocurrency is mined by fixing cryptographic puzzles to generate new blocks. Transactions are broadcast publicly to the community and shared between nodes. Roughly each ten minutes, miners compile these transactions into a brand new block and completely add it to the blockchain, serving because the definitive Bitcoin ledger.
Mining calls for vital computational energy and time because of the complexity of the method. In return, miners earn a small quantity of cryptocurrency. Miners perform like fashionable clerks, recording transactions and gathering transaction charges.
The community makes use of blockchain cryptography expertise to attain consensus on coin possession amongst all contributors.