Using a novel array of back-to-back photodiodes, the sensor carry out properly in poor lighting with out cumbersome equipment or advanced algorithms, promising a leap ahead in high-speed, low-power object recognition.
Researchers on the Hong Kong Polytechnic College have developed a bio-inspired imaginative and prescient sensor able to detecting objects in numerous lighting situations, together with nighttime, shadowed places, and foggy environments. This new sensor, launched in Nature Electronics, can adapt to the spectral options of its surroundings, enhancing object detection reliability in autonomous autos and cell robotic programs.
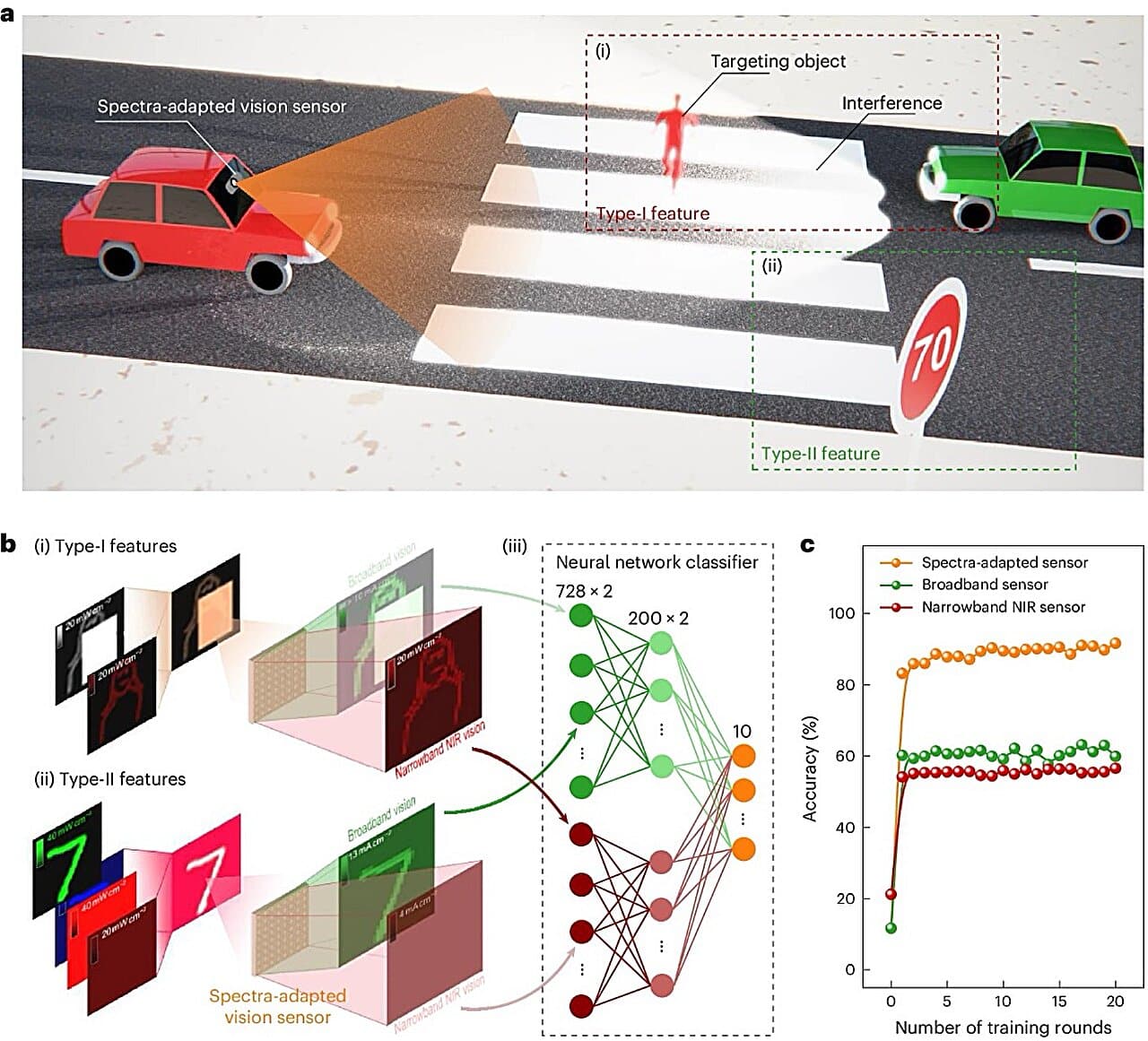
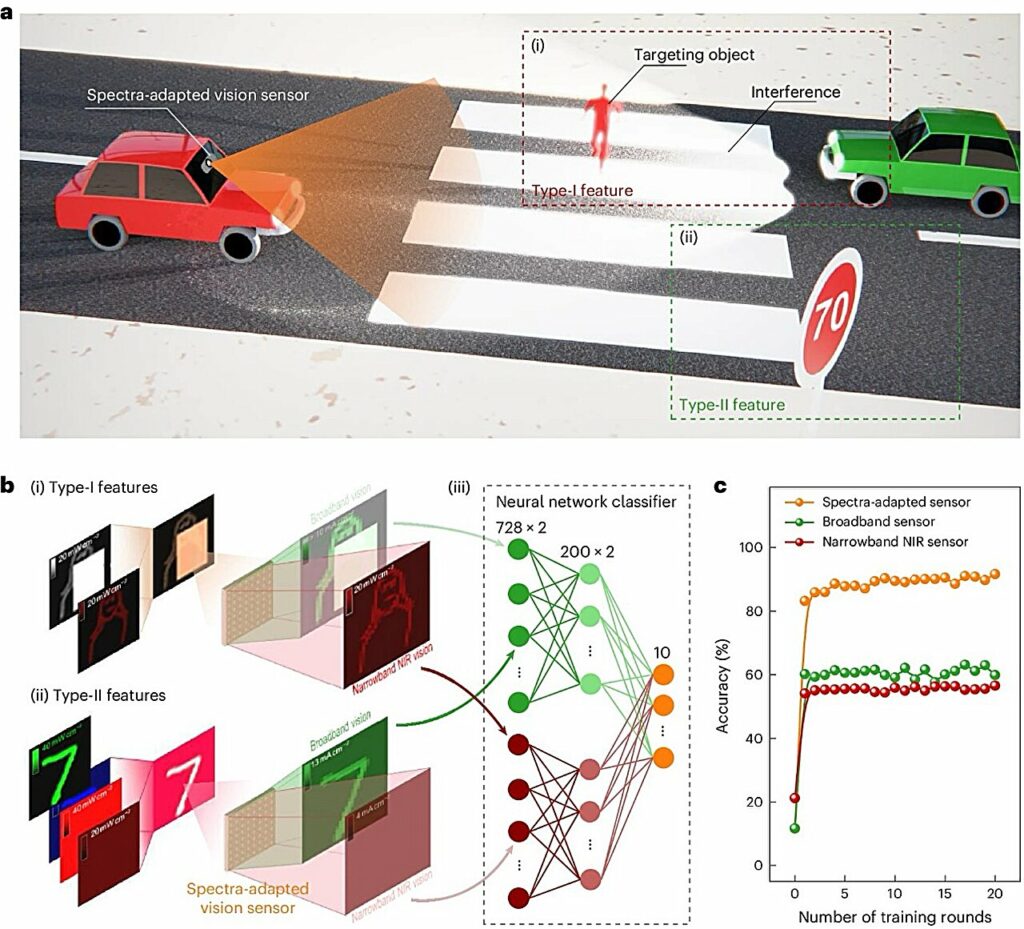
Conventional laptop imaginative and prescient strategies battle beneath poor lighting. The brand new sensor, based mostly on an array of back-to-back photodiodes, addresses this limitation. The researchers aimed to create a sensor that excels in recognizing objects regardless of robust mild interference, smoke, or fog. The design focuses on minimal time latency and low energy consumption with out counting on cumbersome optical equipment or advanced algorithms. The sensor makes use of back-to-back photodiodes with switchable junctions of various spectral sensitivities, managed by an exterior bias voltage. The shallow junction (TiO2/Sb2Se3) is delicate to short-wavelength mild, whereas the deep junction (Sb2Se3/Si) is delicate to long-wavelength mild. This design permits the sensor to regulate to the broadband seen spectrum or a narrowband near-infrared spectrum.
The staff talked about that the spectral adaptation course of takes tens of microseconds, similar to the body fee (round 100 kHz) in high-speed cameras. This adaptation improves recognition accuracy beneath intense visible-light glare. Preliminary exams confirmed promising outcomes, significantly in autonomous automobile imaginative and prescient programs, offering anti-glare capabilities with low latency and energy consumption with no need extra optical equipment or advanced algorithms. They introduce an revolutionary in-sensor spectral adaptation know-how. The method could be very quick, similar to high-speed cameras’ body fee.
This sensor might improve robotic programs’ potential to acknowledge objects in numerous lighting situations with out growing energy consumption. Potential functions embrace autonomous autos, medical units, industrial robots, and surveillance programs. Future analysis will concentrate on bettering the sensor’s efficiency in responsivity, dynamic vary, and response pace, integrating extra sensing capabilities, and creating a large-scale array for a mature synthetic imaginative and prescient chip.