Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan College have created a brand new drug-delivery molecule, a zwitterionic polymer complicated that may assist get plasmid DNA inside cells when injected into skeletal muscle, a vital step within the expression of therapeutic RNA and proteins. The examine is revealed within the journal Biomaterials Science.
The brand new compound is successfully sure to plasmid DNA with out affecting its construction. Injected into mouse muscular tissues, the workforce noticed widespread gene expression.
Drug-delivery techniques underpin lots of the medical breakthroughs of our age. For instance, the COVID-19 vaccine makes use of lipid nanoparticles to encase messenger RNA (mRNA) and carry them into cells by a course of known as endocytosis; as soon as inside, mRNA is launched by way of “endosomal escape” earlier than it’s “translated” by mobile equipment into antigens which provoke an immune response.
However whereas such strategies have been efficiently used, there are nonetheless challenges to be overcome, like undesirable aggregation of the provider. As remedies diversify, researchers are looking out for brand spanking new supply strategies for a wider vary of functions.
A workforce from Tokyo Metropolitan College led by Professor Shoichiro Asayama have been learning using polyions, polymers with an electrical cost, to hold plasmid DNA (pDNA) into cells.
Plasmid DNA will be transcribed to messenger RNA or translated into proteins, making them a flexible car for therapies. Additionally they occur to be negatively-charged polymers which may bind to positively charged polyions.
Nonetheless, merely making a big, positively-charged polymer is way from splendid, since their cost may make them poisonous to cells. Latest efforts have turned to zwitterions, that’s, compounds with a constructive cost on one half and a unfavourable cost on one other.
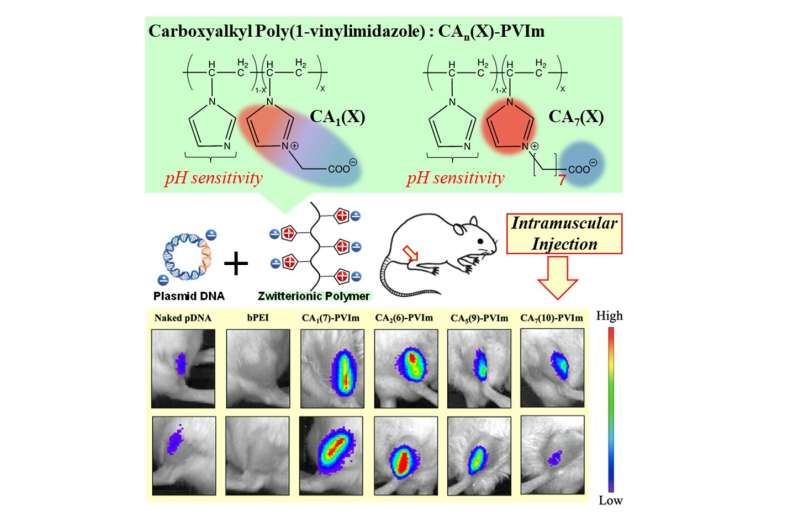
Now, the workforce have engineered the primary zwitterionic polymer compound (CA-PVIm) with an imidazolium cation (constructive cost) which may complicated with pDNA.
Imidazolium teams have the benefit of getting constructive cost smeared out over a hoop of atoms, giving them a great likelihood of binding strongly to pDNA. Negatively-charged parts have been composed of carboxyl teams spaced out by a brief hydrocarbon chain; these have been added into the polymer chain in several proportions.
In preliminary experiments, they discovered that their new compound had a layer of sure water molecules in answer which could render them bioinert. Blended with pDNA, a way used to separate DNA compounds by size was used to point out that pDNA can efficiently complicated with CA-PVIm. Different measurements additionally demonstrated that the complicated hierarchical construction of the pDNA was preserved.
The workforce put their compound to the check by injecting it into the muscle tissue of mice. In comparison with naked pDNA, they discovered gene expression as a result of pDNA over a drastically wider space.
This clearly confirmed that their polyion was being taken up into cells and present process endosomal escape. Additionally they recognized an optimum compound, with 7% of accessible websites given unfavourable costs (CA(7)-PVIm), that gave the best impact.
Since it could possibly ship its cargo over giant plenty of muscle, the workforce’s findings promise new therapies for critical muscular illnesses.
Extra data:
Ren Misaizu et al, Diffusive supply of plasmid DNA utilizing zwitterionic carboxyalkyl poly(1-vinylimidazole) into skeletal muscle in vivo, Biomaterials Science (2024). DOI: 10.1039/D4BM00510D
Offered by
Tokyo Metropolitan College
Quotation:
New and improved drug-delivery molecules for skeletal muscle (2024, July 29)
retrieved 29 July 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-07-drug-delivery-molecules-skeletal-muscle.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.


